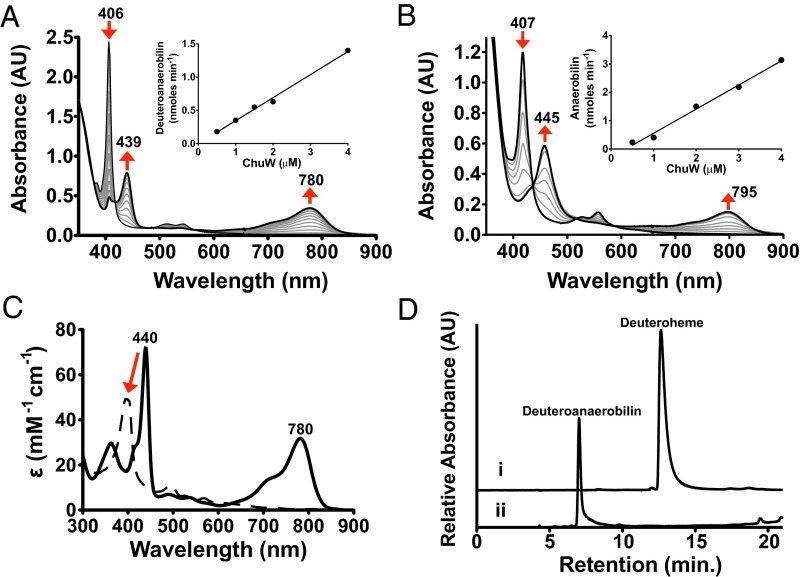
Fig. 2.
Characterization of anaerobic ChuW-dependent heme degradation by UV-visible spectroscopy. UV-visible spectroscopic assays were performed by adding ChuW (2 μM) to a solution containing 10 μM deuteroheme (A) or heme (B), respectively, as well as the EcFld/EcFpr electron donor system (5 and 2 μM, respectively) with 200 μM NADPH. Assays were initiated by the addition of SAM (250 μM), and spectra were recorded every 2 min over the course of 30 min. The red arrows indicate the direction of spectral changes during the course of the experiment. (Insets) Plot of the product formation rate at various ChuW concentrations. (C) The UV-visible spectrum of isolated DAB in methanol resulted in similar spectroscopic features observed in the enzyme assay (solid spectra). Exposure to sunlight resulted in significant changes to the spectra (dashed line). (D) HPLC chromatogram (detection at 397 nm) following the isolation of the deuteroheme substrate and the product of ChuW turnover, herein termed DAB.