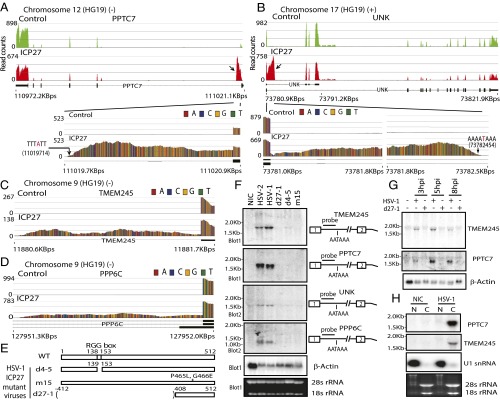
Fig. 1.
HSV ICP27 activates expression of pre-mRNAs prematurely cleaved and polyadenylated from cryptic PASs in intron 1. (A and B) Read counts mapping to representative ICP27-targeted genes in poly(A)-selected RNA PPTC7 (negative strand; A) and UNK (positive strand; B). Control, pFlag vector-transfected cells; ICP27, HSV-2 ICP27-transfected cells. Previously described transcript variants (thick black lines denote exons) are shown underneath. Arrows indicate significant differences in intronic read counts in ICP27-expressing cells. Blowups showing intron 1 read counts are shown below. (C) Blowup showing intron 1 of TMEM245 (negative strand) read counts. (D) Blowup showing intron 1 of PPP6C (negative strand) read counts. (E) Domains and mutations in HSV-1 (WT) and ICP27 mutants d27-1, d4-5, and m15. (F) Northern hybridization of TMEM245, PPTC7, UNK, and PPP6C in HEK293 cells infected with HSV wild-type or ICP27 mutants at 8 hpi using intron-specific probes illustrated at Right to detect prematurely cleaved and polyadenylated pre-mRNAs. β-actin and ribosomal RNAs were used as loading controls. (G) ICP27-mediated prematurely cleaved and polyadenylated mRNAs are detectable during early infection. Northern hybridization for prematurely cleaved and polyadenylated TMEM245 and PPTC7 pre-mRNAs in HEK293 cells infected with HSV-1 KOS strain or d27-1 at 3, 5, and 8 hpi is shown. (H) ICP27-mediated prematurely cleaved and polyadenylated mRNAs can be efficiently exported to cytoplasm. Northern hybridization for prematurely terminated PPTC7 pre-mRNA of cytoplasmic (C) and nuclear (N) RNA fractions from HSV-1 infected at 5 hpi or uninfected (NIC) cells is shown. The same membrane was blotted with probes for PPTC7, TMEM245, and U1 snRNA. U1 snRNA and ribosomal RNAs indicate efficiency of cytoplasmic and nuclear fraction separation.