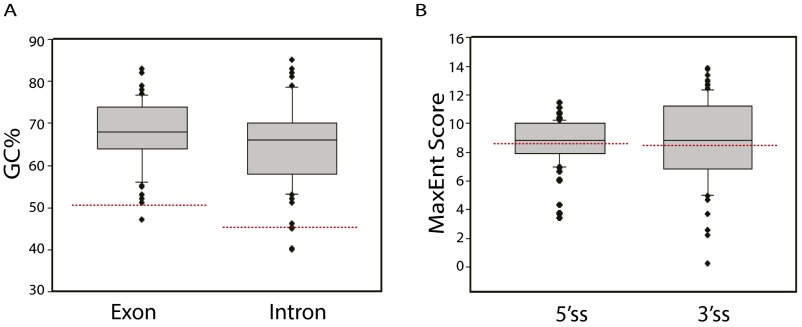
Fig. S5.
ICP27-targeted genes are GC-rich and splice sites are comparable in strength to typical human gene splice sites. (A) The GC content of exon sequences (the intron-proximal 250 bp of the first affected exon or the entire first affected exon sequences if <250 bp), and the GC content of intron sequences (first 250 bp of the affected intron sequences or the entire intron sequences if <250 bp) of 58 ICP27-targeted genes including all genes listed in Table S1 and known ICP27-targeted genes (including ICP34.5, gC and alpha globin) were analyzed. For ICP27-mediated retention of multiple introns, only the most significantly impacted intron was included in the analysis. The median exon GC% and intron GC% was 68.0% and 66.0%, respectively, considerably higher than the GC% of typical human exons (51%) and introns (46%) (shown with red dashed lines). The average exon GC% and intron GC% was 68.0% with 95% CI [65.8%, 70.0%] and 64.5% with 95% CI [62.0%, 67.1%], respectively. (B) Splice sites of ICP27-targeted genes are comparable in strength to the median human gene splice site. The median MaxEnt Score of the 5′ splice site and 3′ splice site of the 58 ICP27 targeted genes was 8.81 and 8.85, respectively, which is comparable to the median MaxEnt score for human 5′ and 3′ splice sites of 8.54 and 8.85, respectively, which are indicated as red dashed lines.