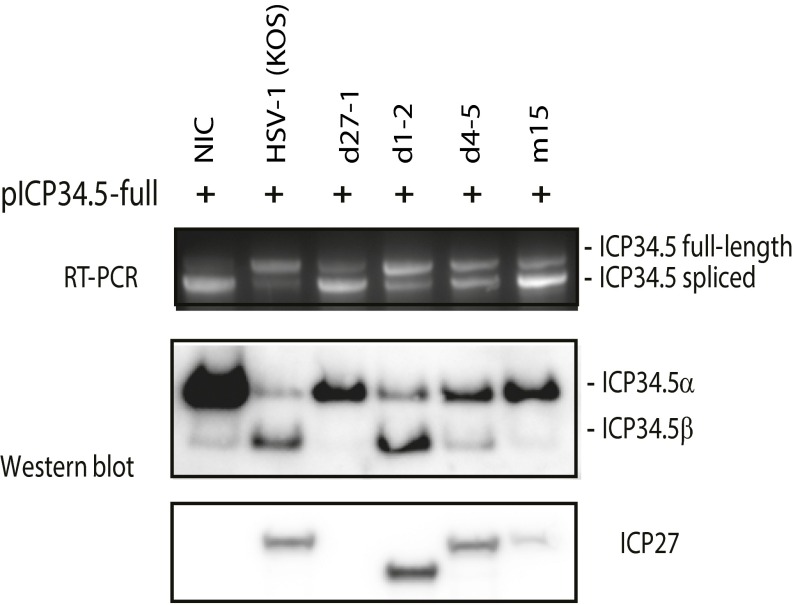
Fig. S8.
HSV-1 inhibits cotranscriptional splicing of HSV-2 ICP34.5. The 293 cells were first transfected with the ICP34.5 expression plasmid (pICP34.5-full). Six hours after transfection, cells were infected with HSV-1 or ICP27 mutants. Both wild-type HSV-1 and d1-2, a HSV-1 mutant with deletion of the N-terminal acid region (with deletion of amino acids 12–63), efficiently inhibited ICP34.5 pre-mRNA splicing (Top) and promoted expression of ICP34.5β protein (Middle). Deletion of the RGG motif (d4-5) modestly reduced the efficiency of ICP27-mediated splicing inhibition but dramatically reduced the expression of ICP34.5 β protein. Mutation of two amino acids of the C-terminal domain (m15) nearly abolished ICP27-mediated splicing inhibition of ICP34.5 and expression of ICP34.5β protein.