Fig. 1.
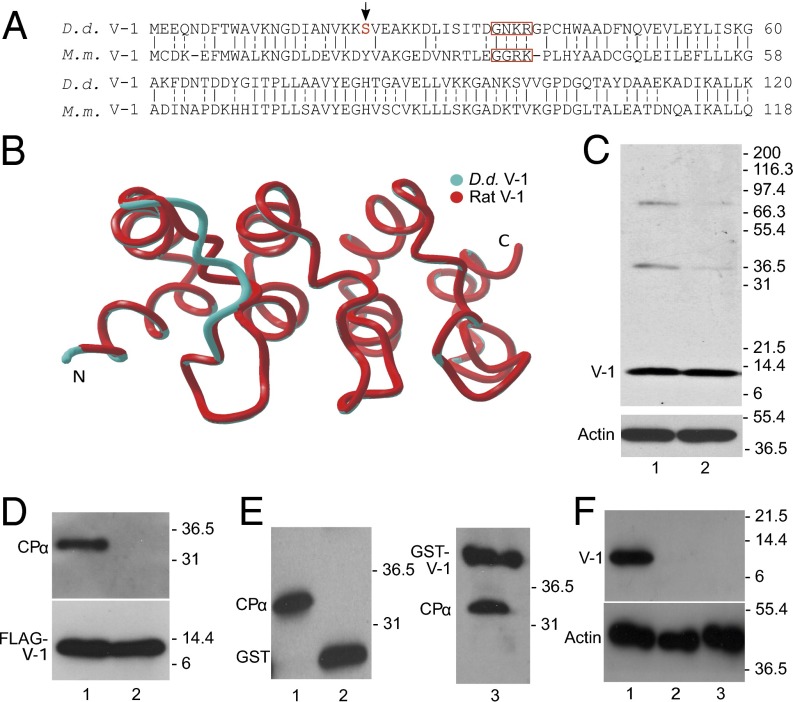
Dictyostelium possesses a V-1 homolog that interacts with CP. (A) Alignment of the amino acid sequences of Dictyostelium (D.d.) and mouse (M.m.) V-1 (identity, solid dash; similarly, split dash). When the boxed residues in M.m. V-1 are mutated to alanine, V-1’s affinity for CP is reduced by ∼200-fold (27). The red S and arrow indicate the phosphorylated serine (Ser-22). (B) Phyre2 homology model of D.d. V-1 (blue) superposed on the experimentally determined backbone structure of rat V-1 (red). (C, Upper) Western blot of whole cell extracts from vegetative (lane 1) and starved, developing cells (lane 2) probed with a polyclonal antibody to D.d. V-1. (C, Lower) Parallel Western blot probed with an antibody to G-actin as a loading control. (D, Upper) Western blot of the material eluted from anti-FLAG M2 beads that had been incubated with lysates of cells expressing FLAG-V-1 (lane 1) or FLAG-FBM V-1 (lane 2) and probed with a polyclonal antibody to D.d. CPα. (D, Lower) Parallel Western blot probed with an antibody to V-1 to demonstrate that approximately equal amounts of FLAG-V-1 (lane 1) and FLAG-FBM V-1 (lane 2) were precipitated. (E) Western blot of the material eluted from agarose beads coated with GST (lane 2) or GST-V-1 (lane 3) that had been incubated with lysates of D.d. amoeba and probed with the antibody to GST-D.d. CPα. The lysate itself is shown in lane 1. Note that the antibody to D.d. CPα also recognizes the GST and GST-V-1 eluted from the column because it was raised against D.d. CPα fused to GST. (F, Upper) Western blot of whole cell extracts from control cells (lane 1) and two independent V-1–null cell lines (lanes 2 and 3) probed with the polyclonal antibody to D.d. V-1. (F, Lower) Parallel Western blot probed with an antibody to G-actin as a loading control.