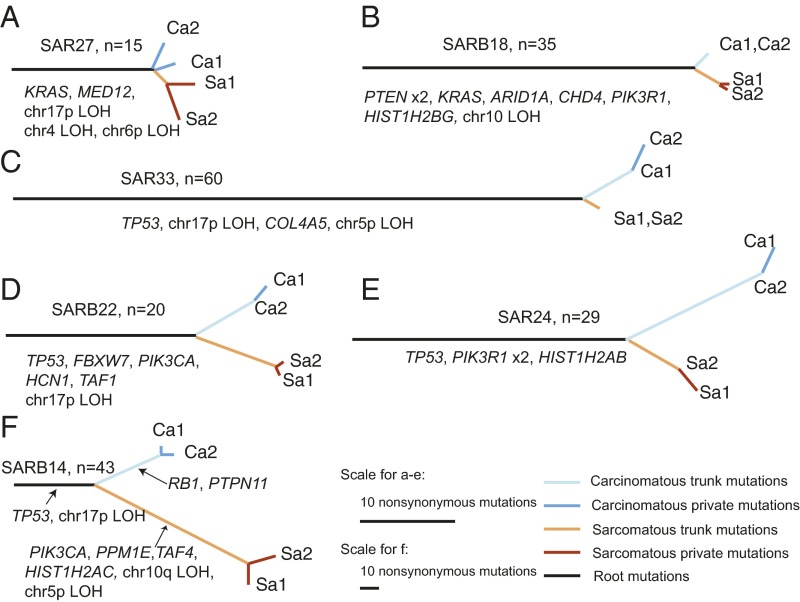
Fig. 3.
Evolution paths of six CSs. (A–F) Each panel shows the phylogenetic tree for one CS tumor that has undergone multiregion sequencing. The tumor name and number of root mutations are indicated at the top of the phylogenetic tree. Ca1 and Ca2 are samples dissected from carcinoma areas, Sa1 and Sa2 are samples dissected from sarcoma areas, root mutations are mutations shared by all samples from the same tumor, sarcomatous (carcinomatous) trunk mutations are mutations shared by all sarcomatous (carcinomatous) samples but never in the carcinomatous (sarcomatous) samples, and sarcomatous (carcinomatous) are private mutations [mutations found in sarcomatous (carcinomatous) samples besides trunk mutations]. Branch length is proportional to the number of nonsynonymous mutations. Driver genes are significantly mutated histone genes, and LOH events are highlighted.