Fig. 2. Schematic representation of interactions between the TLR3 and TLR7 signaling networks.
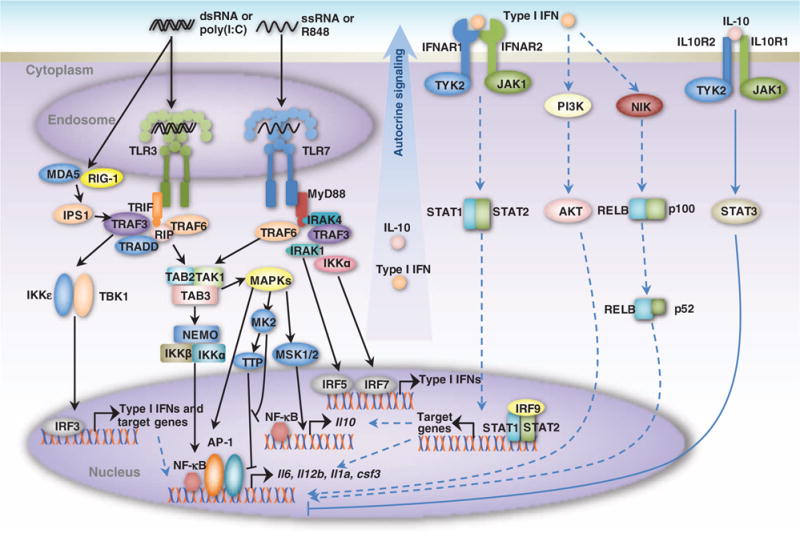
TLR3 recognizes dsRNA [and analogs, such as poly(I:C)] derived from viruses or virus-infected cells and induces the antiviral immune response by promoting the production of type I IFNs and inflammatory cytokines (for example, IL-6 and IL-12p40) through the TRIF-dependent pathway. TLR7 recognizes ssRNA (and analogs, such as R848) and induces the production of type I IFNs and cytokines through the MyD88-dependent pathway. IRF3 and IRF5/7, which are activated by the TLR3 and TLR7 pathways, respectively, lead to the production of type I IFNs. The activation of both NF-κB and AP-1 by both pathways leads to the production of inflammatory cytokines. The detailed reaction schemas are shown in fig. S1.
