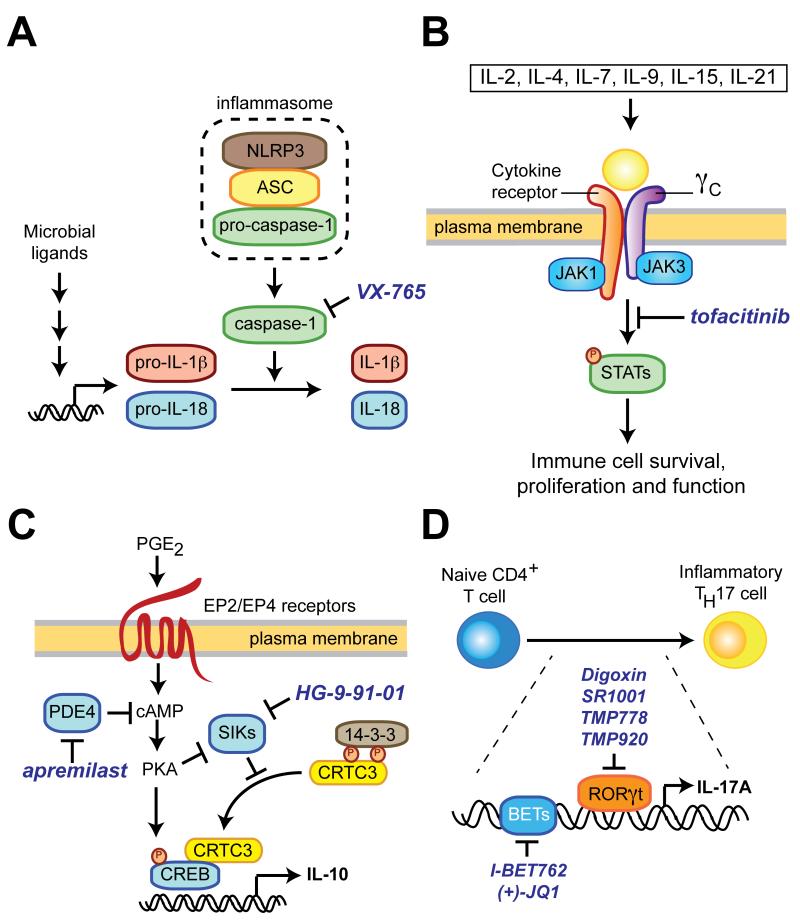
Figure 1.
Representative pathways regulating cytokine production and signaling that have been targeted by small molecules. (A) Microbial stimulation of innate immune cells induces transcription of full-length IL-1β and IL-18. Additional stress signals trigger inflammasome assembly leading to proteolytic processing of IL-1β and IL-18 to their mature forms by caspase-1. VX-765 and other caspase-1 inhibitors specifically block the final stage in this process. NLRP3, NOD-like receptor family, pyrin domain containing 3; ASC, apoptosis-associated speck-like protein containing a carboxy-terminal CARD. (B) The common gamma chain (γc) is a shared component of the receptor for IL-2 and many cytokines and preferentially associates with Janus kinase-3 (JAK3). Stimulation of γc triggers JAK3-dependent phosphorylation of STAT family transcription factors, which leads to pleiotropic effects on immune cell function. Suppression of γc signaling with the small-molecule JAK3 inhibitor tofacitinib is approved therapy for rheumatoid arthritis. STAT, signal transducer and activator of transcription. (C) Salt-inducible kinases (SIKs) restrain IL-10 production by phosphorylation of CRTC3 (CREB-regulated transcriptional co-activator 3), which results in its cytosolic sequestration by 14-3-3 proteins. Stimuli that elevate intracellular cAMP levels (e.g., prostaglandin E2 or PDE4 inhibitors) suppress SIK activity and robustly potentiate IL-10 production by macrophages and dendritic cells, a phenotype that can be mimicked by small molecules that directly inhibit SIKs such as HG-9-91-01. PKA, protein kinase A. (D) Differentiation of inflammatory TH17 cells requires the activity of the transcription factor RORγt and the chromatin-binding BET proteins.