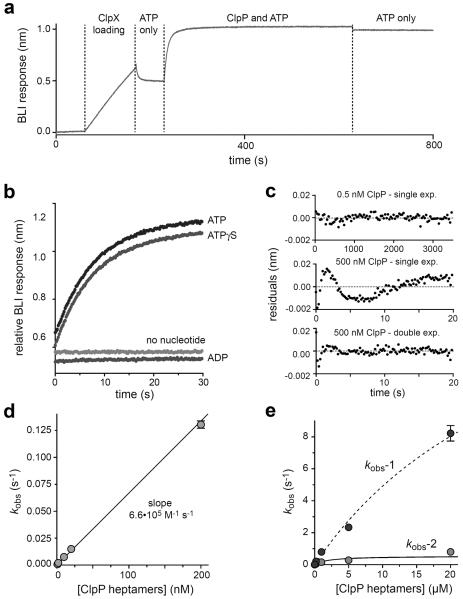
Figure 2.
Association of ClpP with sc6ClpXΔN-bio assayed by BLI. a) A streptavidin-coated BLI biosensor was incubated sequentially with buffer, buffer plus 20 nM sc6ClpXΔN-bio, buffer plus 2 mM ATP, buffer plus 200 nM ClpP and 2 mM ATP, and buffer plus 2 mM ATP. b) BLI trajectories showing that ClpP binding to sc6ClpXΔN-bio occurs with similar kinetics in the presence of ATP or ATPγS (2 mM each). Binding was not observed with 2 mM ADP or no nucleotide. Individual trajectories are offset to allow comparisons. c) Residuals of single-exponential and/or double-exponential fits for association trajectories obtained using ClpP concentrations of 0.5 or 500 nM. d) For ClpP concentrations of 200 nM or less, rate constants from single-exponential fits of ClpP association trajectories (kobs) varied linearly with ClpP, with a slope corresponding to the second-order association rate constant. e) Variation of the rate constants from double-exponential fits for ClpP concentrations of 500 nM or higher. The curves are fits to a hyperbolic equation. For kobs-1 (amplitude ~70%), the maximal rate was 22 ± 7 s−1 with a half-maximal concentration of ~35 μM ClpP heptamer. For kobs-2 (amplitude ~30%), the maximal rate was 0.54 ± 0.2 s−1 with a half-maximal concentration of ~2 μM ClpP heptamer.