Figure 2.
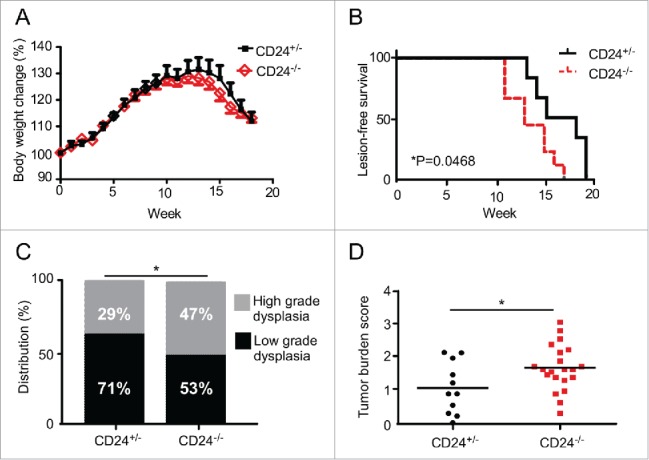
CD24 blunts 4-NQO-induced oral carcinogenesis. (A) CD24−/− and CD24+/− mice were subjected to 50 μg/mL 4-NQO in the drinking water for 16 weeks then switched to regular drinking water. (A) Mouse body weight and (B) tumor lesions of 4-NQO-treated mice (n = 14 CD24+/− and n = 17 CD24−/−) were monitored weekly. Data shown is combined data from two independent experiments with similar findings. (C) The pathology of tongue lesions from CD24−/− (n = 17) and CD24+/− mice (n = 14) was examined. Tumor lesions were classified as low-grade (no tumor or low-grade dysplasia) and high-grade (high-grade dysplasia or invasive cancer). (D) Tumor burden score in the mice was calculated by equally weighting the total number of tongue and oral cavity tumors, tumor size, and histological tumor grade as in Methods section. Using this five-category scoring system, the maximum score obtainable for any animal is five (p = 0.0297). Statistical significance was determined by Chi-square analysis, log-rank test, or two-tailed Student's t-test, where appropriate; *p < 0.05.
