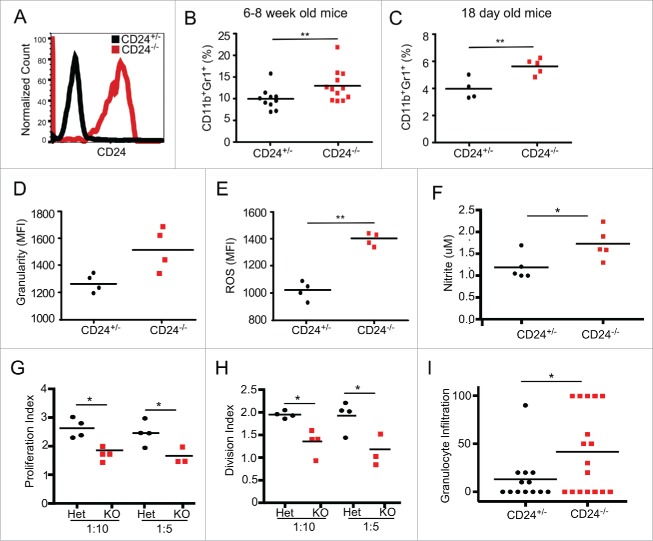
Figure 6.
CD24−/− MDSCs are increased in number and have greater functionality. (A) Cell surface expression of CD24 by peripheral blood CD11b+Gr1+ cells from CD24+/− and CD24−/− mice. (B) Frequency of CD11b+Gr1+ MDSC in the peripheral blood of 6–8 week old CD24−/− mice (n = 12) and CD24+/− mice (n = 10) were analyzed by flow cytometry; (C) Flow cytometric analysis of the frequency of CD11b+Gr1+ MDSC in the spleen of 18 d old CD24−/− mice (n = 5) and CD24+/− mice (n = 4) from the same litter. Flow cytometric analysis of granularity indicated by side scatter profile (SSC) (D), ROS production (E), and nitrite generation (F) by CD24−/− MDSCs. Data is representative of three independent experiments, n = 3–4 mice/experiment. (G-H) CD8+ and MDSCs were MACS isolated from CD24−/+ and CD24−/− mice. CD8+ cells were CFSE labeled and cultured in a 1:5 and 1:10 ratio (MDSC:CD8+) for 3 d. After analyzing CFSE dilution by flow cytometry, the proliferation index and division index were calculated using FlowJo software. (I) Granulocytic infiltration (numbers per 40× high power field) was enumerated in H&E stained tongue lesion sections histologically. Statistical analysis was determined by two-tailed Student's t-test, *p < 0.05 and **p < 0.01.