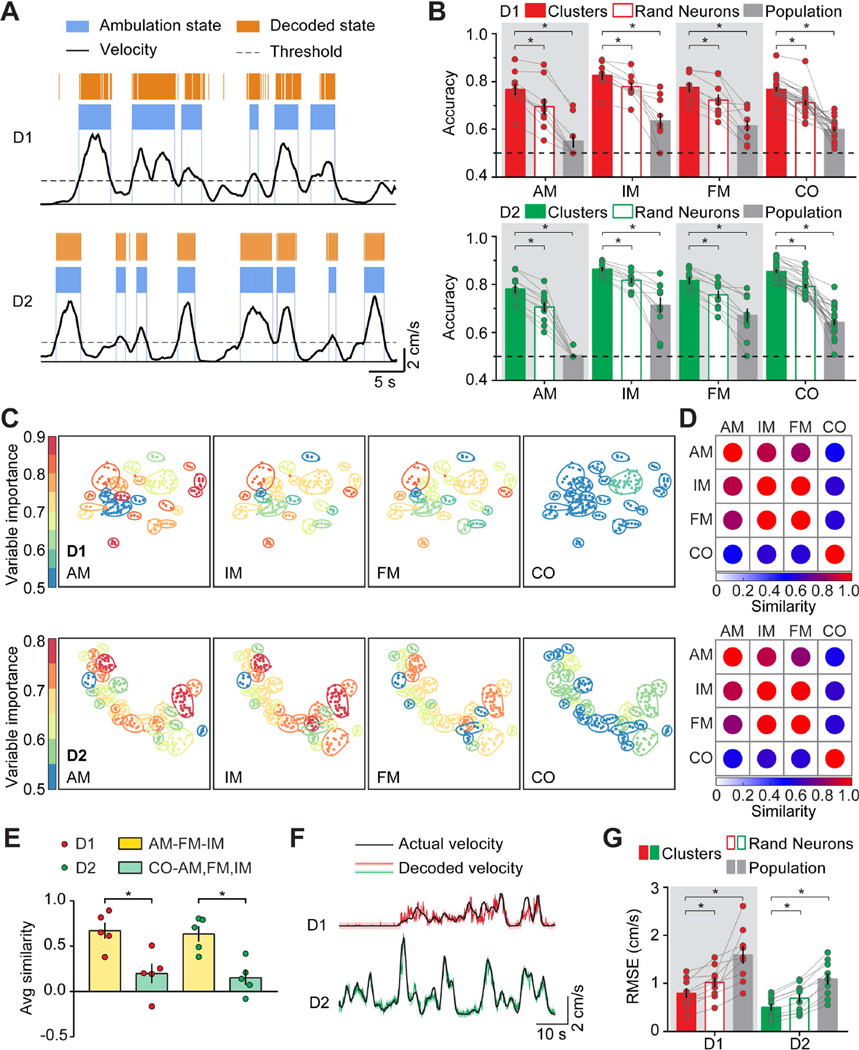
Figure 4. MSN Cluster Activities Perform Better in Behavior Decoding.
A. Mouse ambulation decoding using neural cluster activity data from D1- (Top panel) and D2- (Bottom panel) MSN. Mouse locomotor activity traces were shown at the bottom (Black traces). Ambulation was defined as locomotion velocity higher than 2 cm/s. Blue segments indicated actual ambulation period of mouse; Orange segments indicated prediction of mouse ambulation based on neural cluster activity. Horizontal scale bar: 5 seconds, vertical scale bar: 2 cm/s. B. Histogram showing accuracy of behavior state decoding based on cluster activity (Red filled bars on top panel, D1-MSN; Green filled bars on bottom panel, D2-MSN), randomly selected neuron activities (Red unfilled bars on top panel, D1-MSN; Green unfilled bars on bottom panel, D2-MSN) and population activity (Gray bars on top, D1-MSN; Gray bars on bottom, D1-MSN). Each dot on the plot represented the averaged result from one mouse, and histogram bar represented the mean value for all D1- or D2-mice, with error bars representing sem. AM: ambulation; IM: immobility; FM: fine movement; CO: cocaine. Dotted line at 50% accuracy indicated binary prediction by pure chance. C. Neural cluster map from representative D1-Cre (top panels) and D2-Cre (bottom panels) mouse indicating variable importance value of cluster decoding in four different behavior state decoding. Color on each cluster indicated variable importance value for the cluster in specified behavior decoding experiment, as indicated by the range indicator at the left. D. Similarity matrix for representative D1-Cre (top panel) and D2-Cre (bottom panel) mouse showing similarity of cluster variable importance between any two behavior decoding experiments. Color for the dot in the matrix indicated similarity value, as indicated by the range indicator at the bottom of the matrix. E. Quantification of averaged similarity value between the three normal locomotion behavior states (ambulation, immobility, and fine movement) and the cocaine injection behavior state. Red dots indicated D1-Cre mice, and green dots indicated D2-Cre mice. Each dot on the plot represented the averaged result from one mouse, and histogram bar represented the mean value for all D1- or D2- mice, with error bars representing sem. Yellow histogram bars indicated similarity scores between three normal locomotion behavior states, and green histogram bars indicate similarity scores between normal locomotion states and cocaine injection state. F. Representative mouse locomotion velocity decoding using cluster activity. Black traces indicated the actual mouse locomotion velocity; Red and green traces indicated predicted locomotion velocity based on D1- and D2-MSN cluster activities respectively. Horizontal scale bar: 10 seconds; Vertical scale bar: 2cm/s. G. Quantification of the root-mean-square error (RMSE) between predicted velocity and actual velocity for decoding error based on cluster (Red filled bars, D1-MSN; Green filled bars, D2-MSN), randomly selected neuron activities (Red unfilled bars, D1-MSN; Green unfilled bars, D2-MSN) and population activity (Gray bar at the left, D1-MSN; Gray bar at the right, D2-MSN). Lower RMSE value indicated lower prediction error therefore better prediction. Each dot on the plot represented the averaged result from one mouse, histogram bar represented the mean value for all D1- or D2- mice, with error bars representing sem. Red dots represented D1-Cre mice and green dots represented D2-Cre mice. Asterisk (*) represents statistical significance.