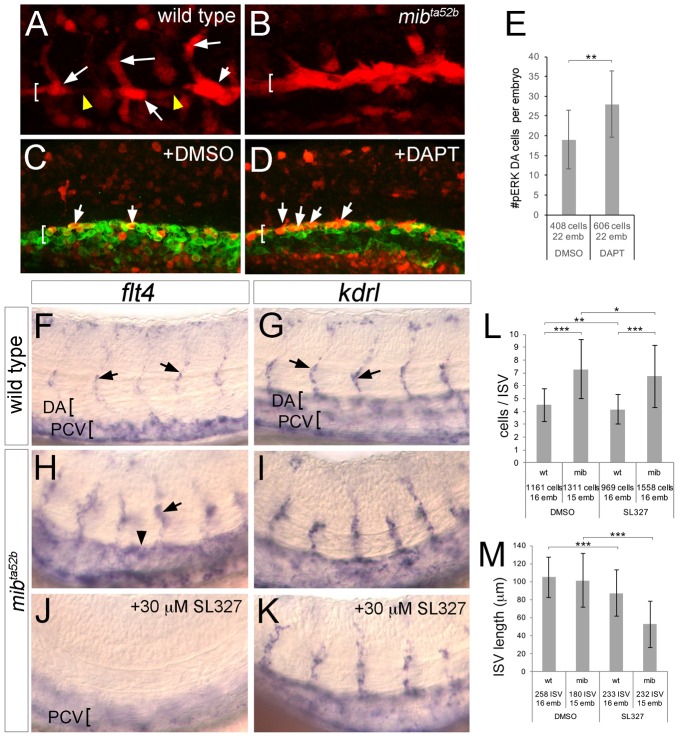
Fig. 7.
Ectopic ERK activation in Notch-deficient embryos induces flt4 and the hyper-angiogenic phenotype. (A,B) Embryos of the indicated genotype at 21 hpf immunostained for pERK (red). (C,D) Tg(fli1a:egfp)y1 embryos immunostained for GFP (green) and pERK (red) at 20 hpf following treatment with the indicated compound from 14 hpf. In A-D, DA is indicated by bracket; arrows denote pERK-positive cells; arrowheads indicate pERK-negative DA cells. (E) Quantification of pERK-positive DA endothelial cells following treatment with DMSO or 100 µM DAPT. (F-K) Whole-mount in situ hybridization with riboprobes against the indicated transcript (top). Arrows denote ISVs; arrowhead shows ectopic DA expression in H. DA and PCV are indicated by brackets. Genotype is noted on the left, chemical treatments are indicated in respective panels. Embryos in J,K were treated with 30 µM SL327 from 25 to 29 hpf. (L,M) Quantification of endothelial cell number per ISV (L) and ISV length (M) in embryos of the indicated genotype and after chemical treatment as indicated. Embryos were treated with 15 µM SL327 from 20 to 34 hpf. (E,L,M) Numbers of cells and embryos used for analysis are shown. Error bars are ±s.d.; *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001.