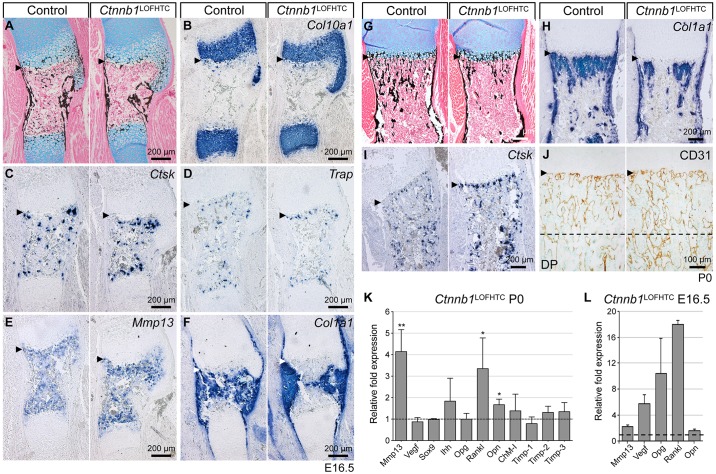
Fig. 1.
Phenotypic analysis of Ctnnb1LOFHTC mouse mutants. (A-F) Representative images of alternating sections through humeri of E16.5 control and Ctnnb1LOFHTC mutant littermates. (A) Alcian Blue/von Kossa staining. (B) Hypertrophic zones visualized by Col10a1 in situ hybridization (ISH). (C) Ctsk ISH. (D) Trap-positive osteoclasts visualized by ISH. (E) Mmp13 ISH. (F) Col1a1 ISH. (G-J) Representative alternating sections through humeri of P0 control and Ctnnb1LOFHTC mutant littermates. (G) Alcian Blue/von Kossa. (H) Col1a1 ISH. (I) Ctsk ISH. (J) Visualization of the vascular network by CD31 (Pecam1) immunostaining. Arrowheads point to the chondro-osseous border. The dashed line indicates the beginning of the diaphysis (DP). (K) qPCR analysis of P0 Ctnnb1LOFHTC relative to control long bone material (n=3). *P<0.05, **P<0.01. Genotype of control in A-K is Ctnnb1fl/+;Col10a1-Cre−. (L) qPCR analysis using E16.5 YFP sorted material from Ctnnb1LOFHTC;RosaYFP/+ long bones relative to material isolated from E16.5 Col10a1-Cre+;RosaYFP/+ limbs (n=2). Error bars indicate s.d.