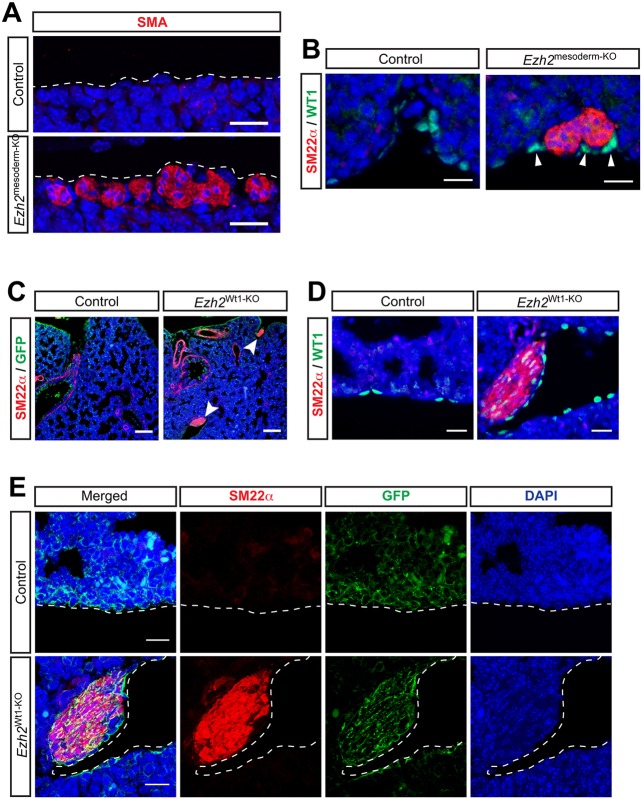
Fig. 5.
Loss of Ezh2 specifically in the lung mesothelium leads to the formation of ectopic smooth muscle nodules. (A) IHC for SMA shows that ectopic smooth muscle forms along the exterior cell layer of the lung at E18.5. (B) Co-IHC for SM22α and WT1 shows that ectopic smooth muscle forms next to the WT1+ mesothelium at E18.5. (C) IHC for SM22α and GFP lineage tracing reveals ectopic smooth muscle (arrowheads) forming in Ezh2Wt1-KO lungs along the GFP+ mesothelium at E18.5. (D) IHC for WT1 and SM22α confirms the close association of ectopic smooth muscle with mesothelium at E18.5. (E) IHC for SM22α and GFP lineage tracing showing colocalization of these markers by confocal microscopy confirms that ectopic smooth muscle arises from the WT1+ lineage in Ezh2Wt1-KO mutants. Scale bars: 20 µm in A,B,D,E; 100 µm in C.