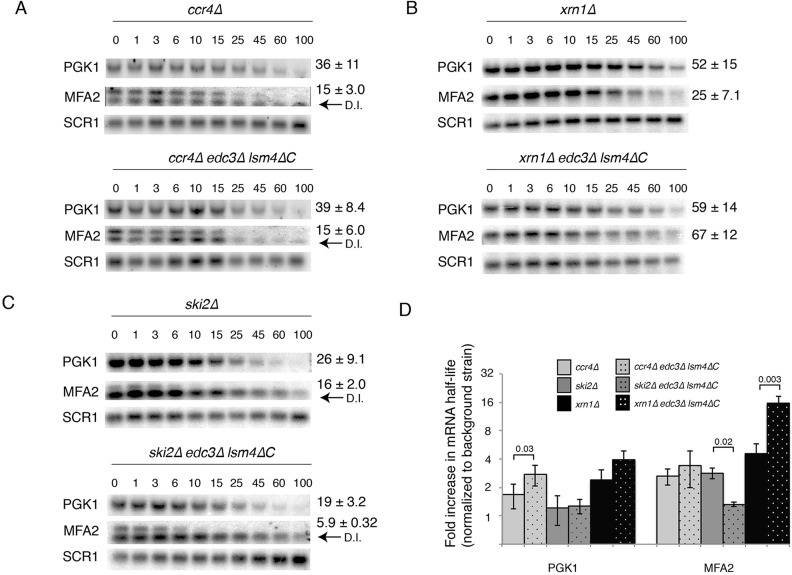
Fig. 3.
Destabilization of mRNA in the edc3Δ lsm4ΔC mutant is attributable to increased deadenylation and decapping-dependent degradation. (A) A CCR4 deletion mutant in the wild-type and edc3Δ lsm4ΔC mutant backgrounds expressing PGK1 and MFA2 mRNA under the control of the GAL promoter when grown in YEP+galactose. Time points (min) indicated are after transcriptional shut-off by addition of glucose. The loading control is SCR1. Error=s.d.; n=5-6 biological replicates. (B) As above, but with an xrn1Δ mutation, PGK1 n=2-3 biological replicates, MFA2 n=3 biological replicates. (C) As above, but with a ski2Δ mutation, PGK1 n=5 biological replicates, MFA2 n=2 biological replicates. (D) A bar graph of PGK1 and MFA2 mRNA half-lives in the strains indicated above in log2 scale. The PGK1 and MFA2 mRNA half-lives were normalized to the wild type or edc3Δ lsm4ΔC strain, respectively. Statistically significant pairings according to a two-tailed t-test indicated with their P values. Error bars indicate standard deviation.