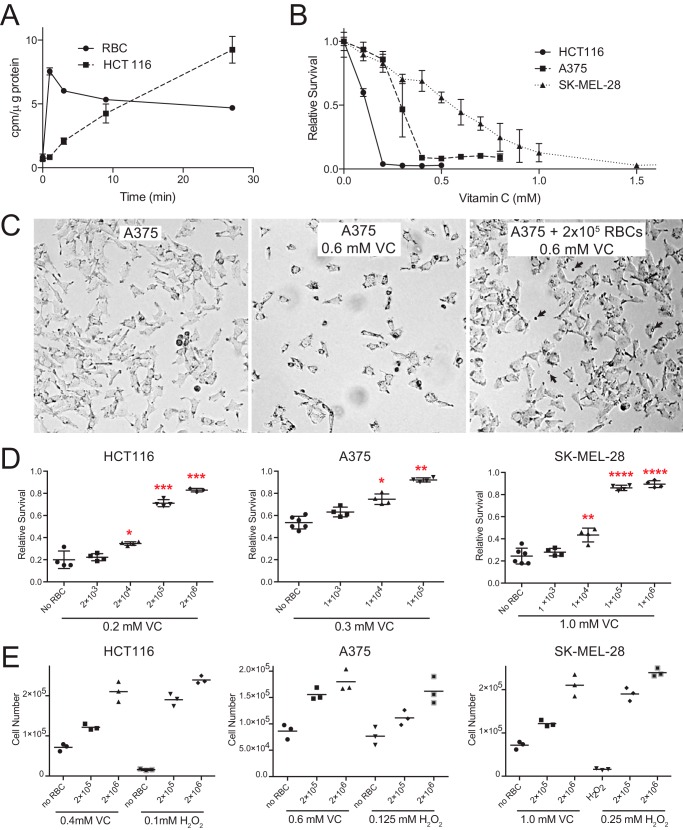
FIGURE 1.
Erythrocytes protect cancer cells from VC and H2O2 toxicity. A, [14C]DHA uptake assay demonstrates that RBCs accumulate DHA more rapidly than HCT116 cells. B, HCT116 and BRAF mutant melanoma cells (A375 and SK-MEL-28) show a dose-dependent toxicity to VC-mediated toxicity as assessed by MTT. C, photomicrographs of A375 cells reveal that VC treatment (0.6 mm for 24 h) caused cytotoxicity. Co-culture with RBCs (indicated by arrows) rescues cell viability. D, the co-culture of RBCs with HCT116, A375, and SK-MEL-28 cancer cells protects them from VC-induced toxicity as assessed by the MTT assay. An equal number of cells cultured without VC or RBCs was used as the reference (100%) to calculate relative survival (n = 3, error bars = S.D.; analysis of variance with Dunnett's correction; *, p ≤ 0.05, **, p ≤ 0.01, ***, p ≤ 0.001, ****, p ≤ 0.0001). E, the co-culture of RBCs with HCT116, A375, and SK-MEL-28 protects them from VC-induced toxicity as assessed by cell number.