FIGURE 4.
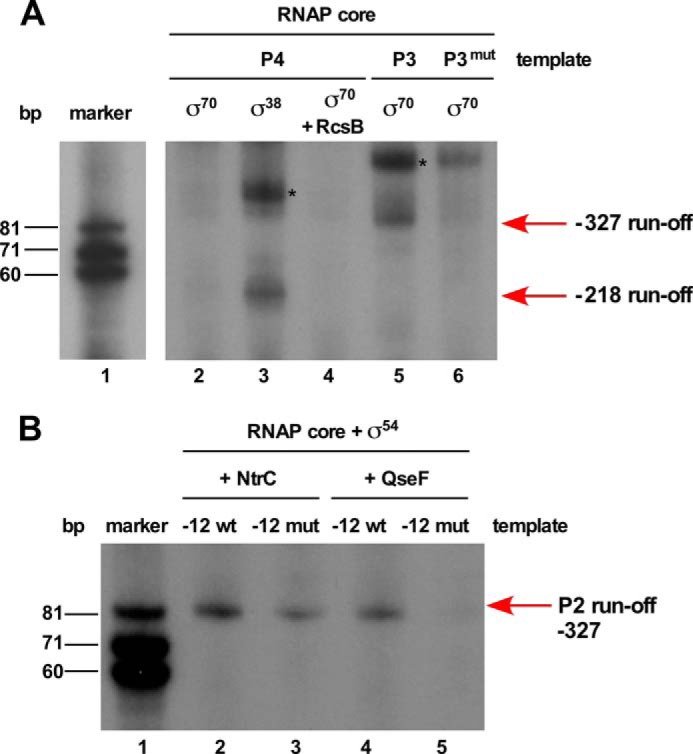
In vitro transcription run-off assays showing selective recruitment of different promoters of the rpoE gene with various forms of RNA polymerase. A, RpoS (σ38) and RpoD complexed with the RNAP core initiate transcription from −218 TSS and TSS at −327, respectively. Lane 1 corresponds to the size standard. For lanes 2–4, a DNA template of 105 bp was used. Lane 2 shows the incubation reaction with Eσ70, lane 3 the incubation with Eσ38 resulting in the synthesis of expected 45-nt product marked with the arrow. Lane 4 was incubated with Eσ70 in the presence of phosphorylated RcsB. Lanes 5 and 6 show RNA transcripts synthesized from DNA template of 170 bp. An expected size of 85-nt RNA product was observed when Eσ70 was incubated with the wild-type DNA template (lane 5), whereas only a weak signal was visible when Eσ70 was used with template with mutation at −7T(C) and −11A(G) in the −10 element (lane 6). Bands marked with an asterisk (*) symbol in lanes 3 and 5 indicate nonspecific end-to-end transcription reaction products. B, RpoN (σ54) complexed with the core RNAP in the presence of either NtrC or QseF can initiate transcription from the rpoEP2 promoter using the −327 TSS. Lane 1 corresponds to size standard, lanes 2 and 4 corresponds to reactions with the wild-type DNA template in the presence of either NtrC or QseF. Lanes 3 and 5 correspond to the RNA transcript produced with DNA template containing mutations at −12 (GC to AT) and −24 (GG to GA).
