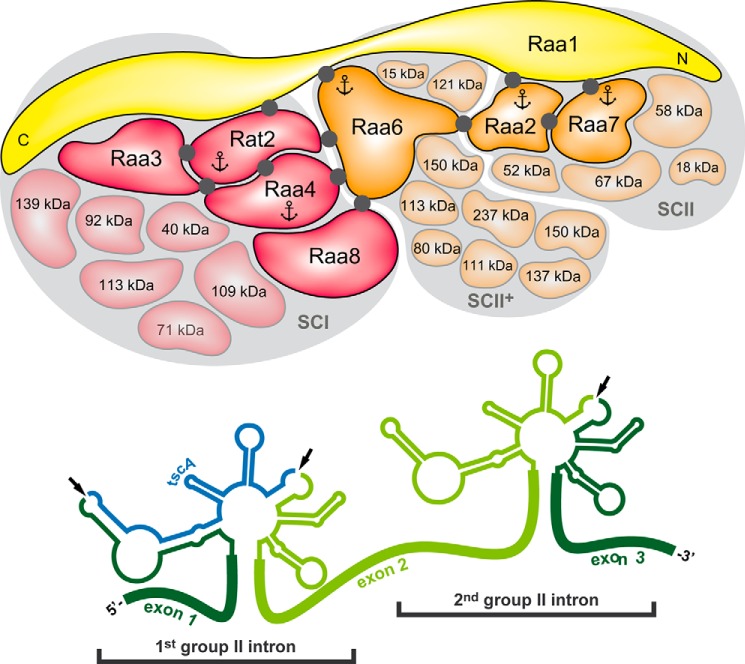
FIGURE 7.
trans-Splicing apparatus of the plastid psaA-mRNA. Depicted are both psaA-mRNA group II introns, psaA-i1 and psaA-i2, with a characteristic secondary RNA structure and identified splicing complexes. Comparative TAP-MS analyses with baits Raa4 and Rat2 led to the identification of subcomplex I (SCI), which is composed of at least 11 core proteins (red; see Fig. 1A). Further, using Raa7 and Raa2 as baits, subcomplex II (SCII) with at least seven core components (orange; see Fig. 1C) was identified. Both subcomplexes share the general splicing factor Raa1 (yellow). Complementation studies showed that the C terminus of Raa1 is involved in psaA-i1 splicing, whereas the central part of the Raa1 protein is essential for splicing of psaA-i2 (21). TAP-MS experiments with bait Raa6 revealed co-purification with Raa2-associated proteins (SCII+; see Table 1) and several core components of subcomplexes I and II. Black dots, direct protein-protein interactions, as detected in yeast two-hybrid analysis (this work; see Ref. 24). Anchors mark proteins that were used as baits in TAP-MS experiments. For clarification, intron RNAs and protein complexes are shown separately, and every splicing factor is present in 1:1 stoichiometry. Dark-colored proteins were previously identified as trans-splicing factors (17–20, 22, 23).