Fig. 8.
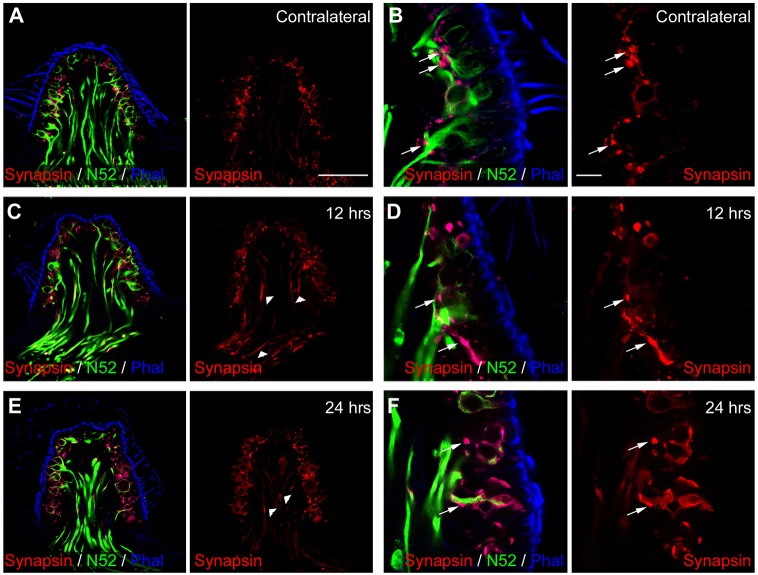
Progression of synapsin expression over time after excitotoxic injury. Immunolabeling in transverse sections of crista observed by performing confocal microscopy. (A,B) In the contralateral ear, counterlabeling of transverse sections with phalloidin (Phal, blue) and antibodies against neurofilament 200 kDa (N52, green) highlight hair bundles of sensory cells and afferent fibers. Immunolabeling with antibodies against synapsin (Synapsin, red) locates small synaptic vesicles in normal vestibular sensory epithelium. (B) High magnification shows precisely that synapsin is expressed in efferent terminals (arrows) contacting afferent fibers. (C,D) At 12 h after the STTK injection, synapsin expression became disorganized and increased. (E,F) At 24 h after the STTK injection, synapsin was also expressed in afferent terminals (arrowheads). Scale bars: 10 µm (A, applies to C,E, and B applies to D,F).