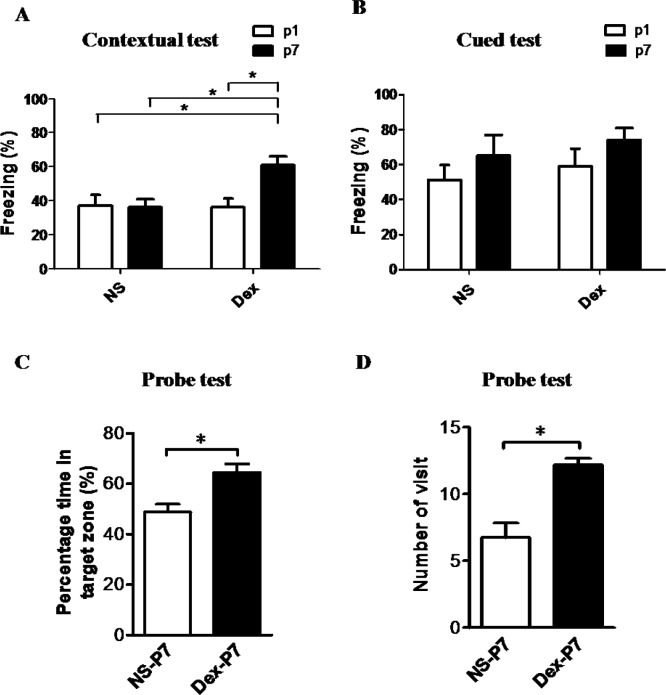
Fig 1. Effects of postnatal administration of dexamethasone (Dex) on fear memory and spatial learning memory formation.
Dex was administered at P1 or P7 and behavioral tasks were performed at P56. (A) The freezing response in contextual fear-conditioning task was significantly greater in the Dex-P7 group than in the other groups (two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni multiple comparisons test, n = 8 for each group *p < 0.05), and Dex-P7 group was significantly greater than NS-P7 group (F[1,28] = 4.59, *p < 0.05). (B) The freezing response in the cued fear-conditioning task was not significantly altered among the four groups (n = 8 for each group). (C) The proportion of time spent searching in target quadrant was significantly higher in the Dex group (64.50 ± 1.50) than in the NS group (48.75 ± 1.56) (Mann-Whitney test, n = 5 for each group, *p < 0.05). (D) The number of crossings in the platform location was higher in the Dex group (12.20 ± 0.22) than in the NS group (6.75 ± 0.55) (Mann-Whitney test, n = 5 for each group, *p < 0.05). The data are expressed as mean ± SEM of three independent experiments.