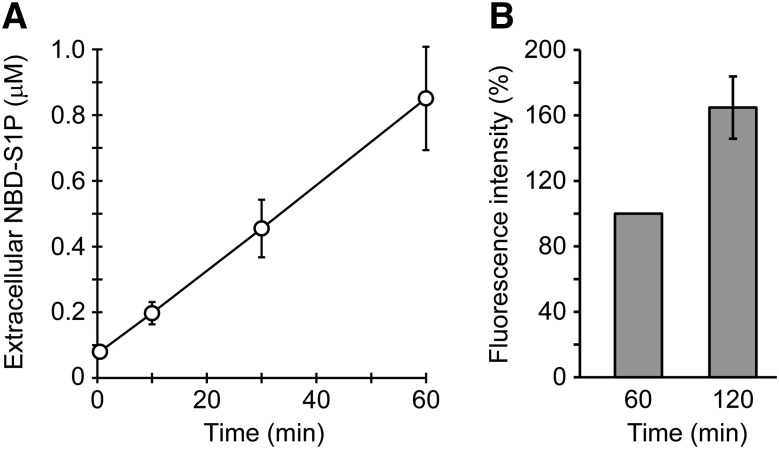
Fig. 6.
Detection of NBD-S1P release from rat erythrocytes by using a microplate reader. A: Rat erythrocytes (5 × 106 cells) were incubated in 100 μl of buffer A containing 0.1% BSA and 5 μM NBD-Sph for the indicated times at 37°C. The lipids in the assay buffer (extracellular) were extracted under alkaline conditions, similarly to Fig. 5C, except that all the reagents were added at half of the original volumes. DMF (40 μl) was added to 160 μl of the aqueous phase, and the fluorescence intensities of the mixtures in a 96-well plate were measured using a fluorescence microplate reader. NBD-S1P standards were prepared to quantify extracellular NBD-S1P (supplemental Fig. S5). Duplicate experiments were performed four times, and the error bars indicate the SD. B: Erythrocytes (1 × 107 cells) were incubated in 200 μl of buffer A containing 0.1% BSA and 5 μM NBD-Sph at 37°C for the indicated times. Then, the assay buffer was separated from the erythrocytes via a brief centrifugation step. The fluorescence intensity of the assay buffer was directly measured using a 96-well plate in a fluorescence microplate reader without lipid extraction. The fluorescence intensity at 60 min was taken as 100%. The experiments were repeated four times, and the error bars indicate the SD.