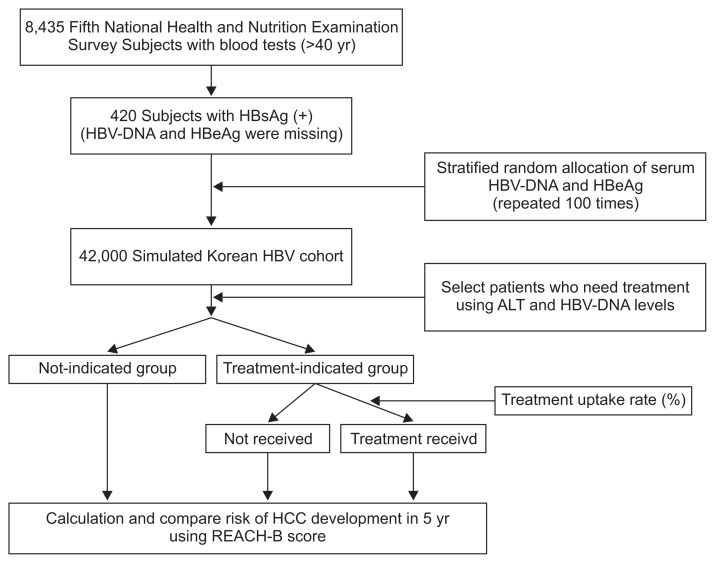
Fig. 1.
Study flow chart. We constructed a Korean hepatitis B virus (HBV) cohort from the fifth National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Because serum HBV DNA levels and hepatitis B e antigen (HBeAg) positivity data were missing, HBV status was allocated randomly according to alanine aminotransferase (ALT) level. The distribution of HBV DNA and HBeAg was simulated using reported data from the Risk Evaluation of Viral Load Elevation and Associated Liver Disease/Cancer study. Random allocation was repeated 100 times. We compared three treatment indication guidelines for antiviral therapy. The risk of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) development in 5 years was calculated using Risk Estimation for HCC in Chronic Hepatitis B (REACH-B) scores.