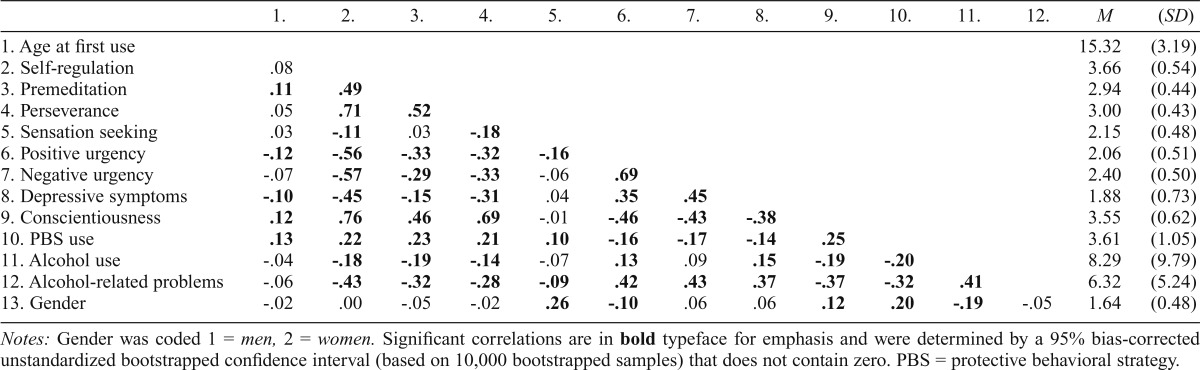
Table 4.
Bivariate correlations among distal antecedents, PBS use, and alcohol outcomes in the comprehensive model
| 1. | 2. | 3. | 4. | 5. | 6. | 7. | 8. | 9. | 10. | 11. | 12. | M | (SD) | |
| 1. Age at first use | 15.32 | (3.19) | ||||||||||||
| 2. Self-regulation | .08 | 3.66 | (0.54) | |||||||||||
| 3. Premeditation | .11 | .49 | 2.94 | (0.44) | ||||||||||
| 4. Perseverance | .05 | .71 | .52 | 3.00 | (0.43) | |||||||||
| 5. Sensation seeking | .03 | -.11 | .03 | -.18 | 2.15 | (0.48) | ||||||||
| 6. Positive urgency | -.12 | -.56 | -.33 | -.32 | -.16 | 2.06 | (0.51) | |||||||
| 7. Negative urgency | -.07 | -.57 | -.29 | -.33 | -.06 | .69 | 2.40 | (0.50) | ||||||
| 8. Depressive symptoms | -.10 | -.45 | -.15 | -.31 | .04 | .35 | .45 | 1.88 | (0.73) | |||||
| 9. Conscientiousness | .12 | .76 | .46 | .69 | -.01 | -.46 | -.43 | -.38 | 3.55 | (0.62) | ||||
| 10. PBS use | .13 | .22 | .23 | .21 | .10 | -.16 | -.17 | -.14 | .25 | 3.61 | (1.05) | |||
| 11. Alcohol use | -.04 | -.18 | -.19 | -.14 | -.07 | .13 | .09 | .15 | -.19 | -.20 | 8.29 | (9.79) | ||
| 12. Alcohol-related problems | -.06 | -.43 | -.32 | -.28 | -.09 | .42 | .43 | .37 | -.37 | -.32 | .41 | 6.32 | (5.24) | |
| 13. Gender | -.02 | .00 | -.05 | -.02 | .26 | -.10 | .06 | .06 | .12 | .20 | -.19 | -.05 | 1.64 | (0.48) |
Notes: Gender was coded 1 = men, 2 = women. Significant correlations are in bold typeface for emphasis and were determined by a 95% bias-corrected unstandardized bootstrapped confidence interval (based on 10,000 bootstrapped samples) that does not contain zero. PBS = protective behavioral strategy.