Figure 1. Eliminating Nox2 reactive oxygen species (ROS) production reduces Mn2+ influx and protects against force decrements in mdx muscle .
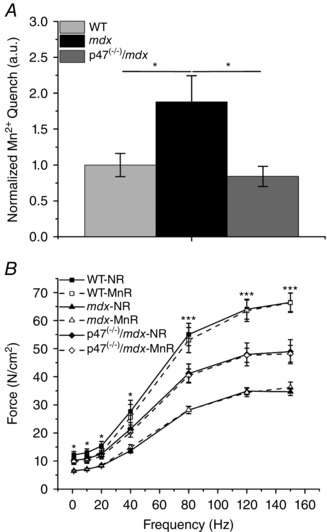
A, sarcolemmal Mn2+ influx is elevated in flexor digitorum brevis fibres of adult mdx skeletal muscle compared with both wild‐type (WT) and p47−/−/mdx muscle, * P ≤ 0.05. B, All three genotypes were significantly different from one another at stimulation frequencies ≥80 Hz, *** P ≤ 0.05. Extensor digitorum longus (EDL) force from WT mice only was greater than that of mdx mice at stimulation frequencies <40 Hz, * P ≤ 0.05. There were no significant differences in force production between EDL muscle in normal Ringer solution (NR; filled symbols and continuous lines) and manganese Ringer solution (MnR; open symbols and dashed lines). Data (means ± SEM) are representative of at least five fibres from at least three animals for Mn2+ quench and at least five animals for force frequency.
