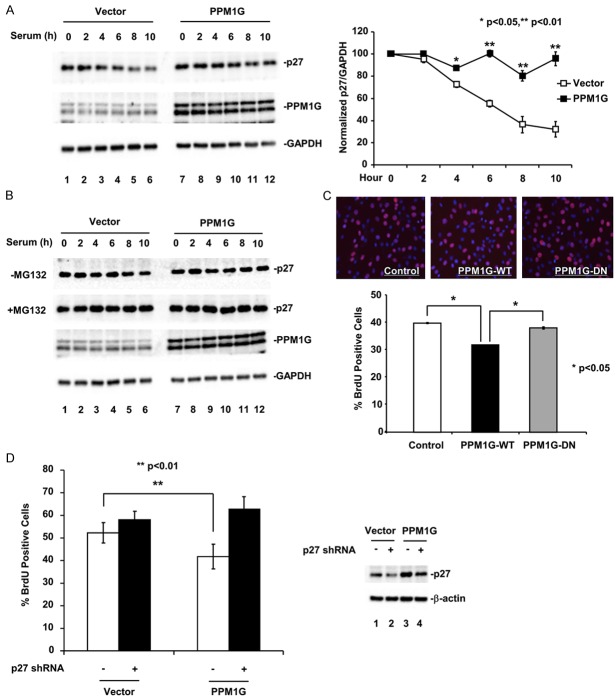
Figure 4.
PPM1G delays cell cycle progression in NIH3T3 cells by stabilizing p27. A. PPM1G increases p27 protein level at G1 phase of the cell cycle. NIH3T3 cells stably expressing PPM1G or control vector were arrested at G0 phase and then released into the cell cycle. Cell lysates were collected and the p27 protein level was determined by Western blot. The results were quantified according to three independent experiments. The p27 protein levels were normalized to GAPDH protein. Values represent the mean of three independent experiments; error bars are ± standard deviation of the mean. P values were determined by student’s t-test. B. PPM1G inhibits the degradation of p27 protein. Experiments are carried out as described in A except that one set of cells was treated with MG132 (10 µM). C. PPM1G delays cell cycle progression in NIH3T3 cells. Cell proliferation was determined using BrdU incorporation assay. Upper panel: BrdU staining. Lower panel: Quantification of BrdU positive cells (total cell number >1,000). P values were determined by one-way ANOVA. D. Knocking down p27 rescues PPM1G-induced cell cycle delay. NIH3T3 cells stably expressing PPM1G or control vector were transfected with control or p27 shRNA. Cell proliferation was determined using BrdU incorporation assay. Left panel: Quantification of BrdU positive cells. Right panel: Western blot of p27. P values were determined by student’s t-test.