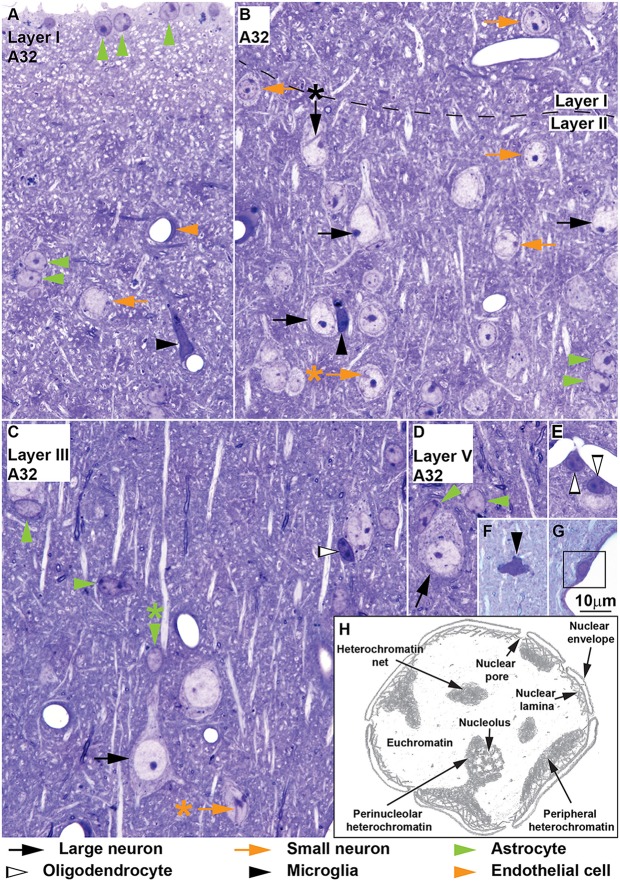
Figure 1.
Neurons and glial cell types in area 32 of the monkey cerebral cortex, semithin sections stained with toluidine blue and sketch of used nuclear structure terms. Large neurons (black arrows) are easy to distinguish because of their large cytoplasm, large “empty” appearing nucleus and prominent nucleolus (B–D); large neurons may show nuclear envelope folding (B, black arrow with asterisk points to folding). The key to distinguishing small neurons (orange arrows) from astrocytes is the constant presence of a patent rim of cytoplasm encircling the nucleus in small neurons (A–C), folding of the nuclear envelope (B,C, orange arrows with asterisk point to folding), absence of thick rim of peripheral heterochromatin and the nucleolus surrounded partially with thick clumps of heterochromatin (B, layer I). The cytoplasm of astrocytes (green arrowheads) is only visible partially with the exception of those astrocytes in layer I forming the glia limitans lining the surface of the cortex (A, vertical green arrowheads); other astrocytes in layer I and in other layers are found in the middle of the neuropil either in pairs (A,B, horizontal green arrowheads) or isolated (C,D, horizontal green arrowheads); some astrocytes are neuron satellite glial cells (C, vertical green arrowhead; D, diagonal green arrowhead) mostly adjacent to neuron bodies, but also to apical dendrites (C, vertical green arrowheads with asterisk). Oligodendrocytes (silhouette arrowheads) have round or ovoid nuclei that are darkly stained with 1–3 thick granules of heterochromatin located in the middle of the nucleus; oligodendrocytes may be satellites to neurons (C) or to blood vessels (E). Microglia (black arrowheads) may have elongated (A) or polylobular (F) nuclei but their nucleus can also be round (B, compared to oligodendrocyte in C); microglial cells may be satellites to blood vessels (A) or to neurons (B) or found in the neuropil (F). (G) Pericytes (surrounded by black square) are found within the basal membrane of the endothelium. (H) Hand drawing of nuclear structures used in the description of Nissl-stained cells. Calibration bar in (G) applies to (A–G).