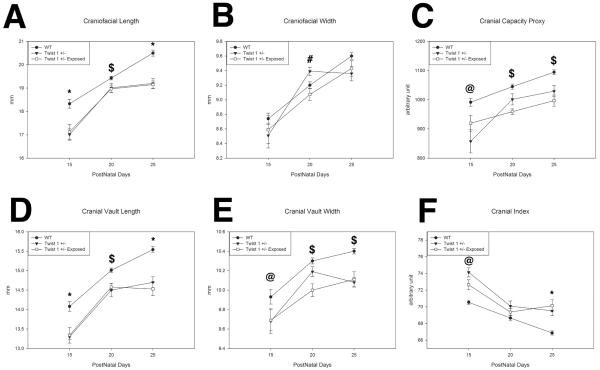
Figure 2. Effects of in utero thyroxine exposure Twist 1 +/− calvarial growth at 15, 20, and 25 days postnatal.
A. Wild types have more craniofacial length than Twist 1 +/− unexposed (p<0.001) and exposed (p=0.027) at 15 days, exposed at 20 days (p=0.032), and both unexposed (p=0.002) and exposed (p<0.001) at 25 days. B. Twist 1 +/− unexposed have greater craniofacial width than exposed (p=0.012). C. Wild types have greater cranial capacity than unexposed at 15 days (p=0.05), and exposed at 20 and 25 days (p<0.001). D. Wild types have greater cranial length than unexposed (p<0.001) and exposed (p=0.05) at 15 days, exposed at 20 days (p=0.001), and unexposed (p=0.002) and exposed (p<0.001) at 25 days. E. Wild types have greater cranial width than unexposed at 15 days (p=0.028), and exposed at 20 (p=0.001) and 25 days (p=0.001). F. Twist 1 +/− unexposed have a larger cranial index than wild type (p=0.023), and both unexposed and exposed have larger cranial indices than wild type at 25 days (p=0.001 and p<0.001). (*) Wild type different from unexposed and exposed. ($) wild type different from exposed. (#) Unexposed is different from exposed. (@) wild type different from unexposed.