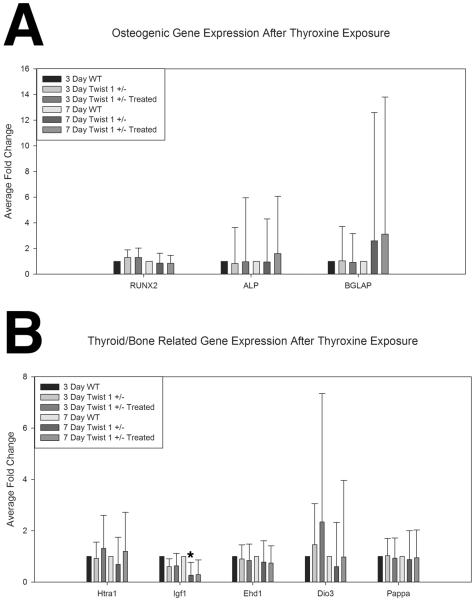
Figure 4. In vitro effects of exogenous thyroid hormone on Twist 1 +/− cranial suture cell gene expression.
A. Osteogenic gene expression from wild type control (n=4), Twist 1 +/− untreated (n=9), and Twist 1 +/− (n=9) cranial suture cells treated with low (7.8ng/ml), medium (78ng/ml), and high (780ng/ml) doses of thyroxine for 3 and 7 days demonstrated a slight modulation of Runx2 activity between control and Twist 1 +/−, a slight increase in Alp associated with treatment, and an increase in Bglap (osteocalcin) expression associated with the Twist 1 +/− genotype. There were no statistically significant differences in the assessed osteogenic gene markers by treatment, group, or time. B. Thyroid related gene expression for all three groups of cranial suture cells demonstrated a slight effect of treatment for Htra1 as compared to wild type control and Twist 1 +/− untreated, and significantly more Igf1 expression in wild type control cells (*). Some modulation of Ehd1, and Dio3, were noted by treatment and genotype, but none was statistically significant. There was no significant change in Pappa gene expression noted between groups, or across times. Error bars reflect standard error of the fold change. Wild Type Control Samples measure of dispersion are included in Supplemental Table 1.