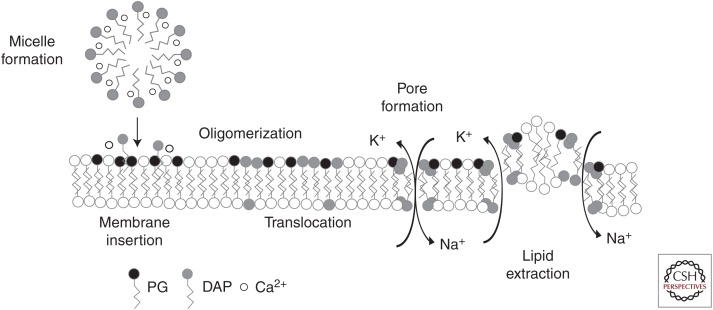
Figure 2.
Proposed mechanisms for the action of daptomycin. In solution, daptomycin (DAP) complexes with calcium to form small micelles, and subsequent membrane insertion is dependent on both the presence of calcium and phosphatidylglycerol (PG). Once inserted, DAP oligomerizes and transitions to the inner membrane leaflet. These complexes then align on opposite sides of the membrane to form a pore channel permeable to small cations, or disrupt membrane integrity by extracting lipids and leading to transient ion leakage.