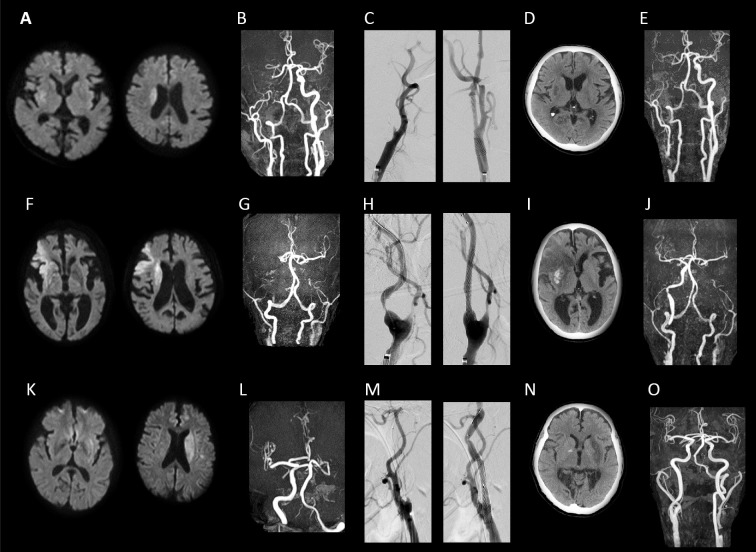
Figure.
Imaging findings of the three cases. Case 1: A-E. A: Diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) on arrival showed acute cerebral infarction in the right basal ganglia extending to the corona radiata, B: Magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) on arrival showed an occlusion of the right internal carotid artery, C: Before and after stent placement, D: Computed tomography (CT) at 24hours after t-PA showed no hemorrhagic change, E: MRA on the 4th hospital day showed reocclusion due to in-stent thrombosis. Case 2: F-J. F: DWI on arrival showed acute cerebral infarction in the right frontal temporal lobe and corona radiata, G: MRA on arrival showed a bilateral occlusion of the internal carotid artery, H: Before and after stent placement, I: CT at 24 hours after t-PA showed a hemorrhagic change in the right basal ganglia, J: MRA on the 5th hospital day. The carotid stent was patent. Case 3: K-O. K: DWI on arrival showed acute cerebral infarction in the left basal ganglia extending to the corona radiata, L: MRA on arrival showed an occlusion of the left internal carotid artery, M: Before and after stent placement, N: CT at 24 hours after t-PA showed no hemorrhagic change, O: MRA on the 14th hospital day. The carotid stent was patent.