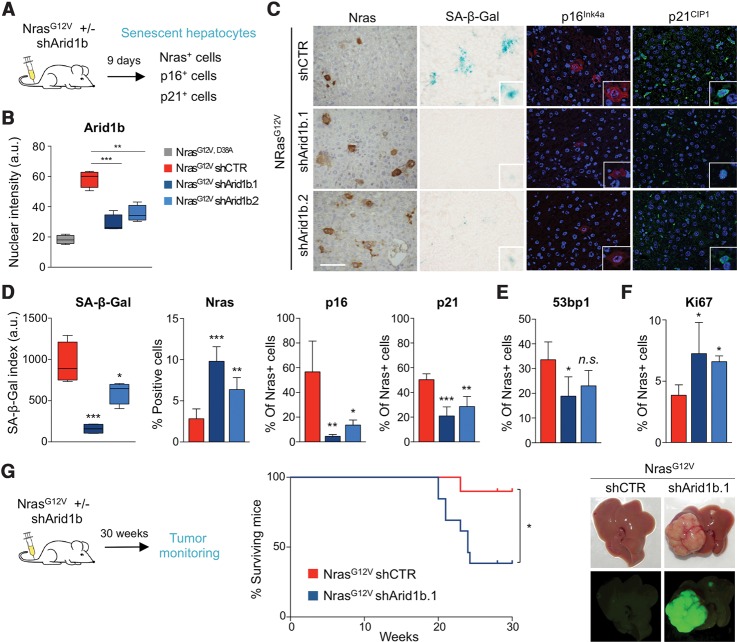
Figure 2.
Knockdown of Arid1b alleviates OIS in vivo and cooperates in HCC formation. (A) Scheme of the in vivo senescence experiments. Transposon constructs carrying NrasG12V cDNA and Arid1b shRNAs (or control) were delivered into mouse livers by hydrodynamic injection (NrasG12V/D38A was used as negative control). n = 4 mice per condition were used. (B) Quantification of Arid1b nuclear IF staining in Nras+ mouse hepatocytes in the above-described conditions is shown. (C) Representative pictures of immunohistochemistry (IHC) for Nras, SA-β-Gal staining, and IF staining for p21CIP1 and p16INK4a on liver sections from mice injected with the indicated vectors. (D–F) Quantification of the SA-β-Gal staining and percentages of Nras-positive, p16INK4a-positive, or p21CIP1-positive cells (D) and 53bp1-positive (E) or Ki67-positive (F) cells in liver sections from mice injected with the indicated vectors. Graphs represent mean ± SD from n = 4 mice. (***) P < 0.001; (**) P < 0.01; (*) P < 0.05; (n.s.) nonsignificant by two-tailed Student t-test. (G, left) Scheme of the in vivo tumor growth experiment. Transposon constructs carrying NrasG12V cDNA and an Arid1b shRNA (or control) were delivered into mouse livers by hydrodynamic injection. Mice were monitored for 30 wk. n = 10 shCTR and n = 13 shArid1b.1 mice were used. Kaplan-Meier survival curves (middle) and representative pictures of livers (right) showing GFP-positive tumor nodules as they were derived from the injected constructs. (*) P < 0.05 by log rank (Mantel-Cox) test. Bar, 100 μm. DAPI was used to visualize the nuclei.