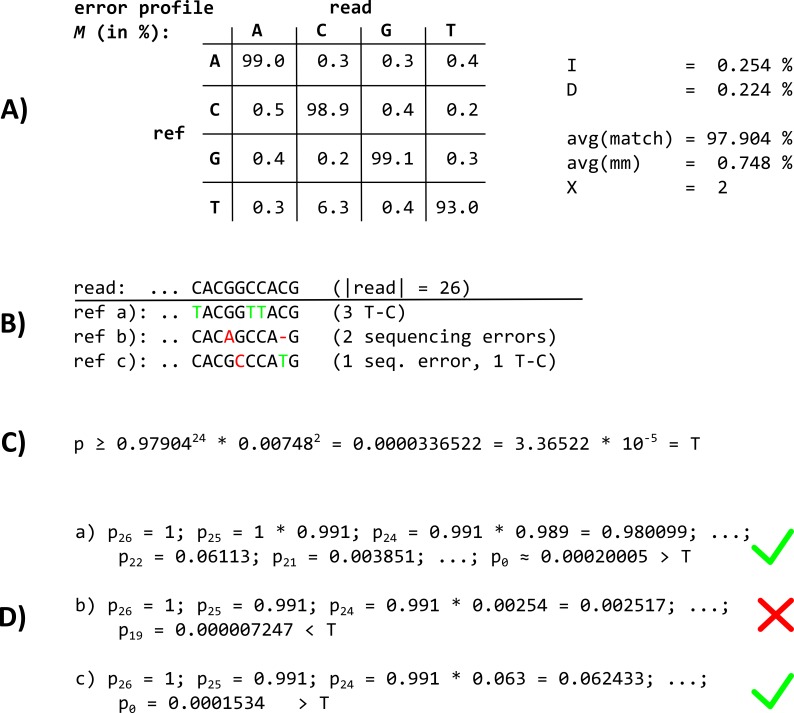
Figure 4. The BWA PARA alignment approach.
(A) The error profile probability matrix M and the indel probabilities I and D, which are used as input for the BWA PARA algorithm, as well as exemplary results of the intermediate calculations of the BWA PARA algorithm. In M, only T–C conversions have a higher probability (6.3%) than sequencing errors and indels. (B) The last characters of a particular read and three examples of mapping positions within a reference, called ref a–c. (C) The calculation of a maximum threshold T for the mapping probability p (see the Equation 2 in the main text, and values from (A) in this image). (D) The mapping probability calculation of the read when mapped to References a–c. The read fails to map against ref b with two sequencing errors, whereas ref a and ref c are suitable mapping positions, where the probability p is higher than the threshold T. For implementation, we worked with the open-source read aligner BWA (version 0.7.8) to extend its algorithm for the alignment of short and error-prone reads.