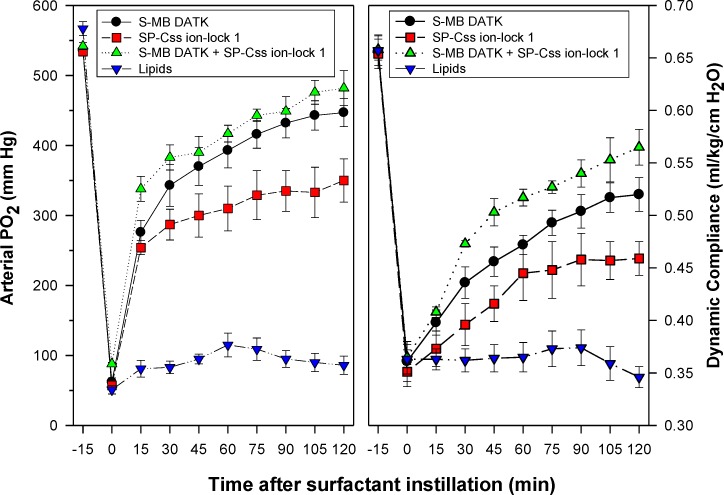
Figure 6. Physiological activity of synthetic surfactants containing glycerophospholipids and SP-B/C peptides in ventilated rabbits with ARDS-related lung injury induced by in vivo lavage.
Synthetic surfactants containing lipids (5:3:2 DPPC:POPC:POPG) combined with 1.5% S-MB DATK + 1.5% SP-Css ion-lock 1 peptides or 3% of either peptide alone, were instilled intratracheally to rabbits meeting clinical oxygenation criteria for ARDS. All glycerophospholipid/peptide surfactants significantly improved oxygenation (arterial PO2) and dynamic compliance (mL/kg/cm H2O) in rabbits over a study period of 120 min compared to lipid-only controls (P < 0.05). However, the greatest pulmonary improvements were found for the dual-peptide surfactant preparation containing 1.5% S-MB DATK + 1.5% SP-Css ion-lock 1 (P < 0.05 for both oxygenation and dynamic compliance compared to either single-peptide surfactant). Data are Mean ± S.E.M. for N = 5–9 per treatment group.