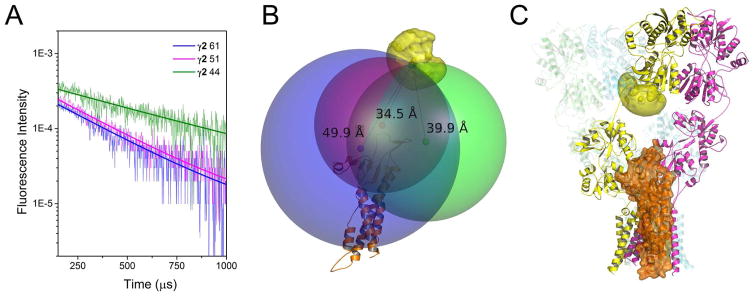
Figure 2. LRET-Nanopositioning system-based model of AMPA receptor-stargazin interaction.
A) LRET lifetimes between GluA2 amino-terminal domain site 128 of the apo AMPA receptor and sites 44 (green), 51 (magenta) and 61 (blue) in the extracellular region of stargazin (γ2) are shown. See also Figure S1. B) Stargazin homology model (orange) with the root mean positions of its fluorophores shown as red, green, and blue hard spheres. The LRET-determined distances to the donor fluorophore (39.9 Å for γ2 site 44, 34.5 Å for γ2 site 51, and 49.9 Å for γ2 site 61) were used to generate the larger spheres. The AMPA receptor structure and stargazin model were positioned to place the terbium fluorophore at the point of intersection of the LRET-radii spheres. C) Our model of the means of interaction between the AMPA receptor and stargazin. See also Figure S3