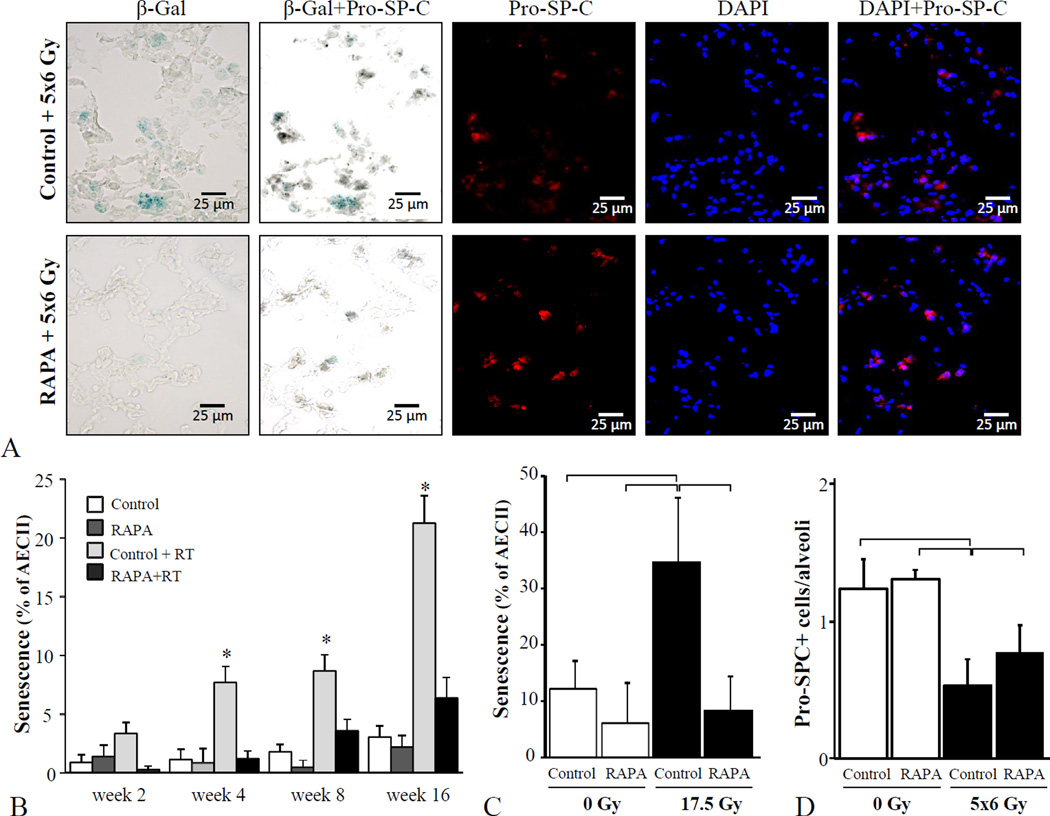
Figure 5. Rapamycin reduces AECII senescence after irradiation.
Lung tissue from C57BL/6NCr mice treated with 5×6 Gy of thoracic IR and control or rapamycin formulated diet was collected after IR (n=3 per condition). The percentage of type II pneumocyte (AECII) cells (stained by Pro-SP-C) staining for β-Gal activity at 2, 4, 8, and 16 weeks after IR was scored. A) Representative images at week 16 after IR, B) Percentage of AECII co-stained with Pro-SP-C at 16 weeks after IR. C) Primary pneumocyte cultures were treated with rapamycin (0, 50 ng/ml) or vehicle for one hour prior to IR (17.5 Gy). Cells were fixed after 3 days and co-stained for β-Gal and pro-surfactant C (pro-SPC). The percent of pro SP-C stained cells that stained for β-Gal were scored. D) The number of AECII per alveolus was scored in mouse lung at 16 weeks after IR. Bars: mean; error bars: standard error; *p < 0 .05 for the comparison to rapamycin+5×6 Gy treatment at the same time point by ANOVA.