Figure 3.
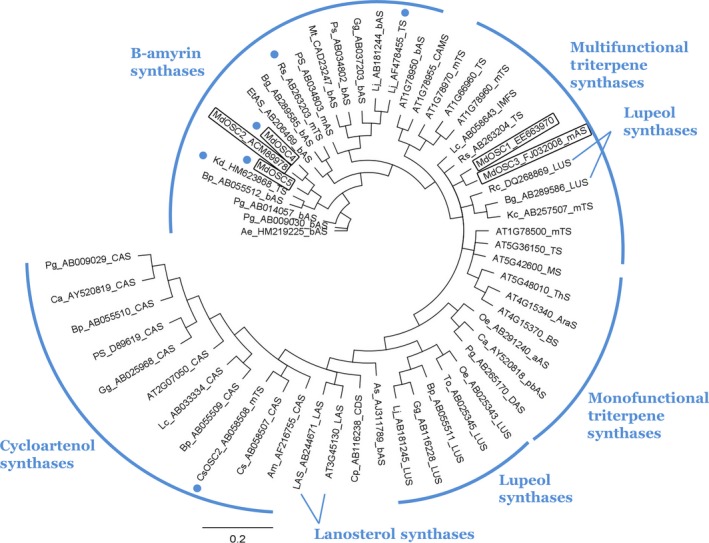
Phylogenetic tree of a wide range of triterpene synthase amino acid sequences, built using the neighbour‐joining method. Sequences were selected from GenBank based on their authentication in the literature (unless otherwise indicated). The scale bar indicates 0.2 amino acid substitutions per site. The GenBank or The Arabidopsis Information Resource (TAIR) identifier is included in the gene name. The two‐letter prefix for each name in the tree identifies the species name as follows: Ab, Abies magnifica; Ae, Aralia elata; As, Avena strigosa; Bg, Bruguiera gymnorhiza; Bp, Betula platyphylla; Ca, Centella asiatica; Cp, Cucurbita pepo; Cs, Costus speciosus; Et, Euphorbia tirucalli; Gg, Glycyrrhiza glabra; Kc, Kandelia candel; Kd, Kalanchoe daigremontiana; Lc, Luffa cylindrical; Lj, Lotus japonicas; Mt, Medicago truncatula; Oe, Olea europaea; Pg, Panax ginseng; Rc, Ricinus communis; Rs, Rhizophora stylosa; To, Taraxacum officinale. Measured triterpene activities are encoded in the suffix for each entry name as follows: aAS, alpha amyrin synthase; AraS, arabidiol synthase; bAS, beta‐amyrin synthase; BS, baruol synthase; CAMS, camelliol c synthase; CAS, cycloartenol synthase; CDS, cucurbitadienol synthase; DAS, dammarenediol‐II synthase; IMFS, isomultiflorenol synthase; LAS, lanosterol synthase; LUS, lupeol synthase; mAS, mixed amyrin synthase (both alpha and beta amyrin); MS, marneral synthase; mTS or TS, multifunctional terpene synthase; pbAS, putative bAS; ThS, thalianol synthase. Multifunctional triterpene synthases within monofunctional triterpene synthase groups are marked with a bullet.
