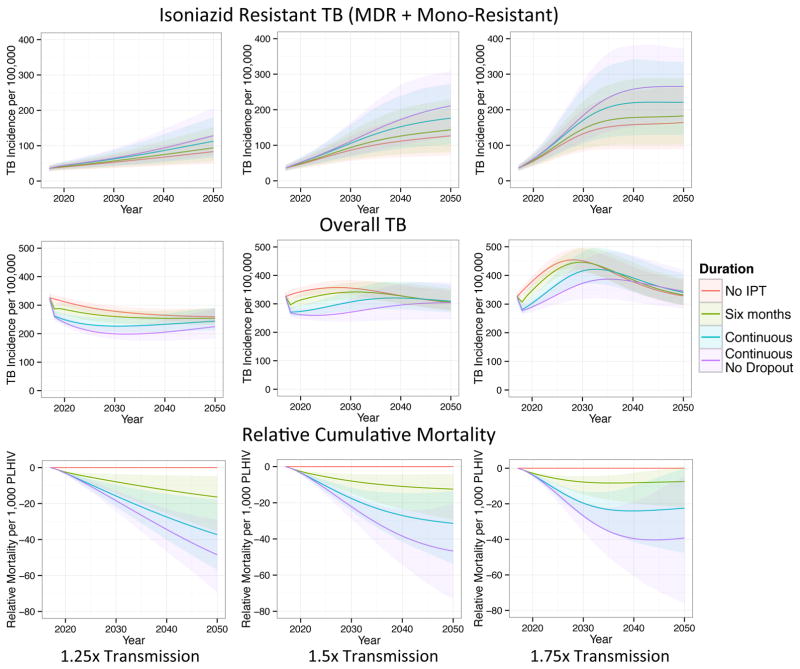
Figure 4.
The effects of IPT duration on the incidence of isoniazid resistant and overall TB (new cases per year) and cumulative mortality relative to no IPT (cumulative deaths per 1,000 PLHIV) when the transmission parameter post-2017 is increased 1.25x, 1.5x, and 1.75x compared to our baseline scenario. When transmission is relatively high, longer durations of IPT can produce large increases in the incidence of isoniazid resistant TB, eroding their initial overall incidence benefits. Solid lines display means and shaded regions display 95% quantiles of our posterior predictions.