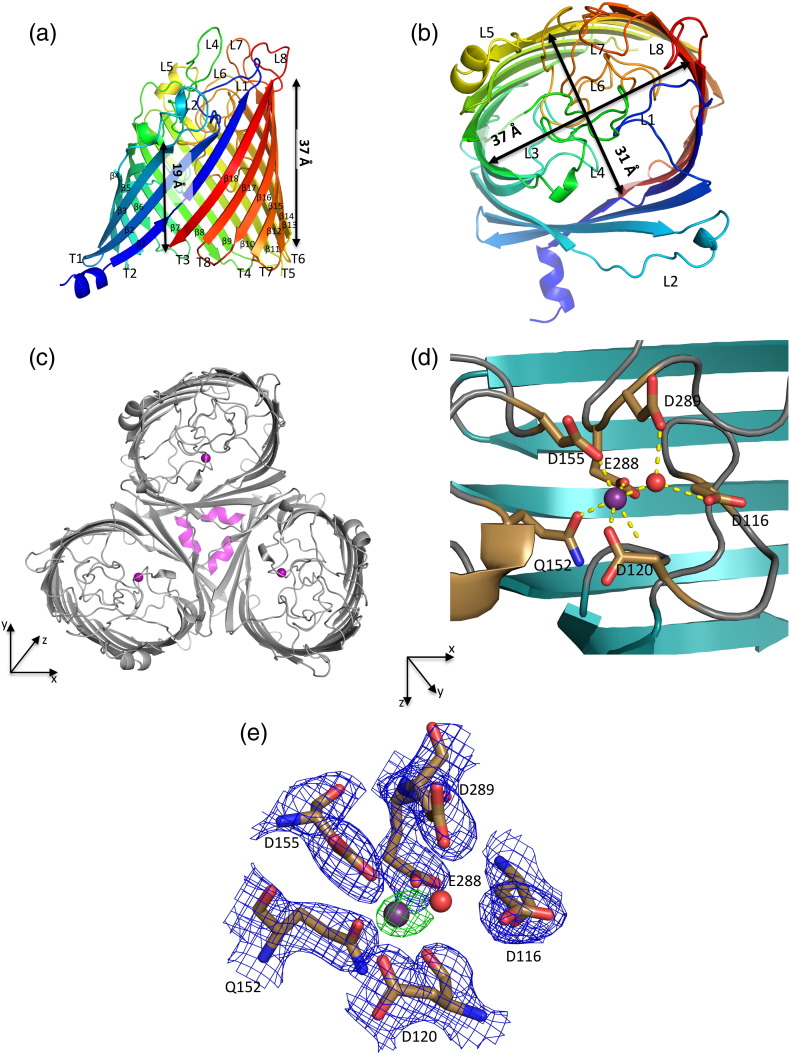
Fig. 1.
The structure of the MOMP monomer. (a) Viewed from the side, parallel to the membrane. (b) The structure has been rotated 90° so that it is viewed from the outside of the cell (looking in), perpendicular to the membrane. (c) The trimer viewed as in (b), the periplasmic N-terminal α-helix is colored magenta and the calcium in purple. An XYZ axis is shown to orientation. (d) The calcium is depicted as a purple sphere and the water molecule as a red sphere. Residues involved in the calcium coordination are shown as sticks. An XYZ axis shows the view that has been rotated by 90° around the X axis when compared to (c). (e) A detailed view of the amino acids involved in calcium-binding site; same orientation as in (d). The Fo-Fc and 2Fo-Fc electron density maps at 5σ and 2σ, respectively, have shown the final refined coordinates. The phases for the calculation of the map were based on a model that had never included the metal ion.