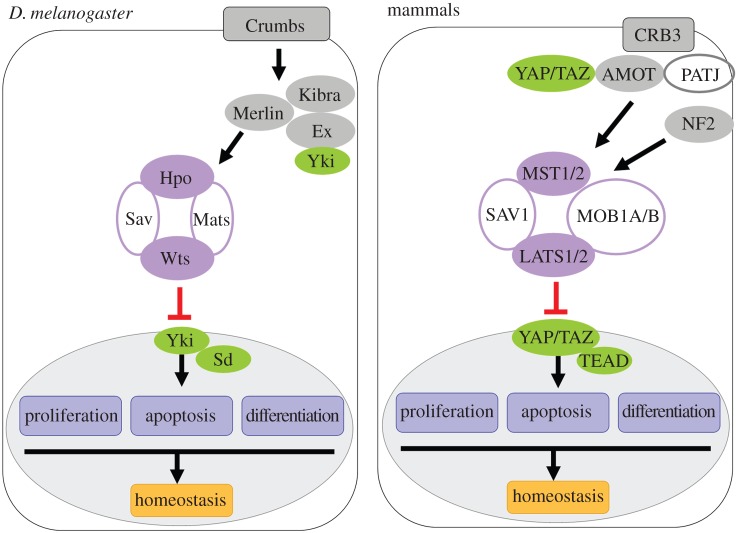
Figure 1.
Models of Hippo pathway in fly and mammals. A simplified version of Hippo pathway regulation is shown here. In both Drosophila and mammals, when Yki/YAP/TAZ is relieved from inhibition through phosphorylation-dependent or independent mechanisms, its nuclear translocation then drives target gene expression in regulation of cellular proliferation, apoptosis and differentiation. The phosphorylation mechanism relies on the core kinase cascade including Hpo/MST, Wts/LATS, Sav/SAV1 and Mats/MOB1. In Drosophila, the FERM domain protein Ex has been shown to physically associate with Yki and block its nuclear translocation. Similarly, in mammals, the adherens protein AMOT and CRB3 complex inhibit target gene expression via sequestering YAP/TAZ in cytoplasm.