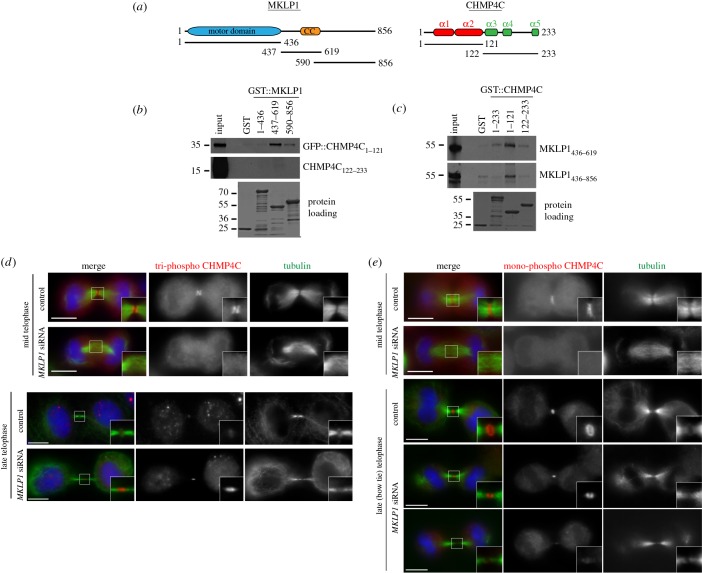
Figure 6.
MKLP1 binds directly to CHMP4C and is required for its localization to the central spindle during cytokinesis. (a) Schematic diagrams illustrate the protein domains of MKLP1 and CHMP4C. The CHMP4C α-helices are marked at the top. The positions of the different MKLP1 and CHMP4C fragments used for the in vitro pull-down assays are also indicated. CC, coiled coil. (b) The GST::MKLP1 protein fragments shown at the top and GST alone were incubated with the in vitro translated and radiolabelled CHMP4C polypeptides indicated at the right, and then pulled down using glutathione beads. The Ponceau S staining of the protein loading is shown at the bottom and the numbers on the left indicate the sizes (kDa) of the molecular mass markers. (c) The GST::CHMP4C protein fragments shown at the top and GST alone were incubated with the in vitro translated and radiolabelled MKLP1 polypeptides indicated at the right, and then pulled down using glutathione beads. The Ponceau S staining of the protein loading is shown at the bottom and the numbers on the left indicate the sizes (kDa) of the molecular mass markers. (d) HeLa Kyoto cells were treated with siRNAs directed against either a random sequence (control) or KIF23/MKLP1 and after 48 h fixed and stained to detect triphospho CHMP4C (red), tubulin (green) and DNA (blue). DNA condensation and nuclear shape were used as criteria to stage telophase cells. Insets show two times magnifications of the central spindle and midbody. Scale bars, 10 µm. (e) HeLa Kyoto cells were treated with siRNAs directed against either a random sequence (control) or KIF23/MKLP1 and after 48 h fixed and stained to detect mono-phospho CHMP4C (red), tubulin (green) and DNA (blue). DNA condensation and nuclear shape were used as criteria to stage telophase cells. Insets show two times magnifications of the central spindle and midbody. Scale bars, 10 µm.