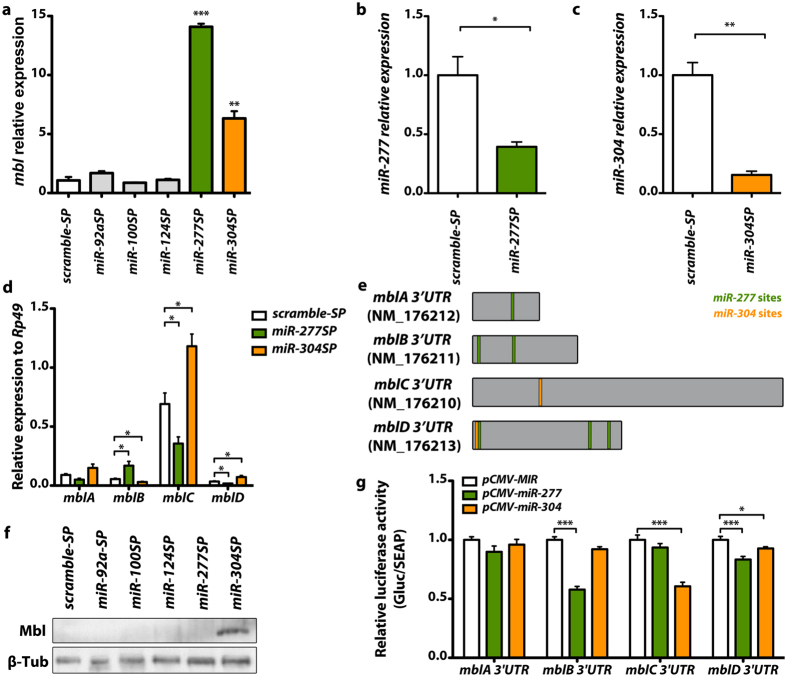
Figure 1. Tissue-specific silencing of dme-miR-277 and dme-miR-304 upregulates muscleblind mRNA and protein in Drosophila muscle.
(a) qRT-PCR amplification of muscleblind from flies expressing miRNA sponge constructs for dme-miR-92a, dme-miR-100, dme-miR-124, dme-miR-277 and dme-miR-304 in muscle. muscleblind expression levels were strongly upregulated in miR-277SP and miR-304SP flies. (b) Analysis of the levels of muscleblind isoforms by qRT-PCR. dme-miR-277 silencing in muscle caused an upregulation of the mblB isoform whilst expression levels of the mblC and mblD isoforms were reduced in miR-277SP flies. Conversely, mblC and mblD levels were increased and the mblB isoform was reduced in miR-304SP flies. (c) Detection of Muscleblind protein by Western blot. An increase of Muscleblind protein was only detected in miR-304SP flies. All the indicated transgenes were driven in muscle using Mhc-Gal4. Histogram showing dme-miR-277 (d) and dme-miR-304 (e) relative expression levels according to qRT-PCR data. Both miRNAs were significantly silenced in flies expressing the corresponding sponge constructs under the control of Mhc-Gal4 compared to flies that expressed scramble-SP (control). (f) Scheme of the predicted binding sites for dme-miR-277 and dme-miR-304 in muscleblind 3′ UTRs (mblA to mblD). Reference sequence accessions and size (in nt) are also included. Representation is to scale. (g) Quantification of Gaussian luciferase activity relative to alkaline phosphatase (Gluc/SEAP) of HeLa cells cotransfected with the indicated mbl 3′ UTR sensor constructs and plasmids expressing dme-miR-277 or dme-miR-304. Significantly reduced relative luminescence compared to empty vector (pCMV-MIR, control) reveals direct binding of dme-miR-277 to mblB and mblD 3′UTRs and of dme-miR-304 to mblC and mblD 3′ UTRs. The graphs show means±s.e.m. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 (Student’s t-test).