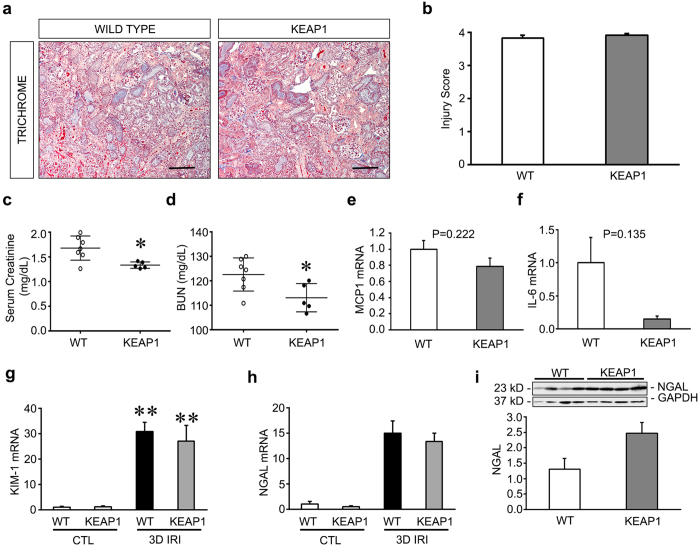
Figure 2. Keap1 hypomorphs have improved renal function 3 days after ischemia-reperfusion injury (IRI).
Wild type (WT) and hypomorph mice (KEAP1) were subjected to unilateral renal IRI, with a contralateral nephrectomy performed 24 hours prior to sacrifice at 3 days. (a,b) Histologic assessment of kidneys showed significant tubular injury with no perceptible difference between groups. Bar equals 100 μm. (c,d) Serum creatinine and BUN were significantly improved in the hypomorphs in spite of the lack of histologic differences. Each dot represents an individual animal with mean ± SEM shown. (e,f) qRT-PCR showed no significant reductions in proinflammatory mediators (n = 4–5 in each group). (g,h) qRT-PCR analysis of tubular injury markers KIM-1 and NGAL showed a significant increase (KIM-1) or trend to increase (NGAL) in injured kidneys vs CTL uninjured kidneys, but no significant difference between injured WT and KEAP1 kidneys. (j) Western blot and densitometry for NGAL confirms no decrease in NGAL in injured KEAP1 kidneys compared to injured WT kidneys. (*P < 0.05 compared to the wild type group. **P < 0.05 compared to either CTL group).