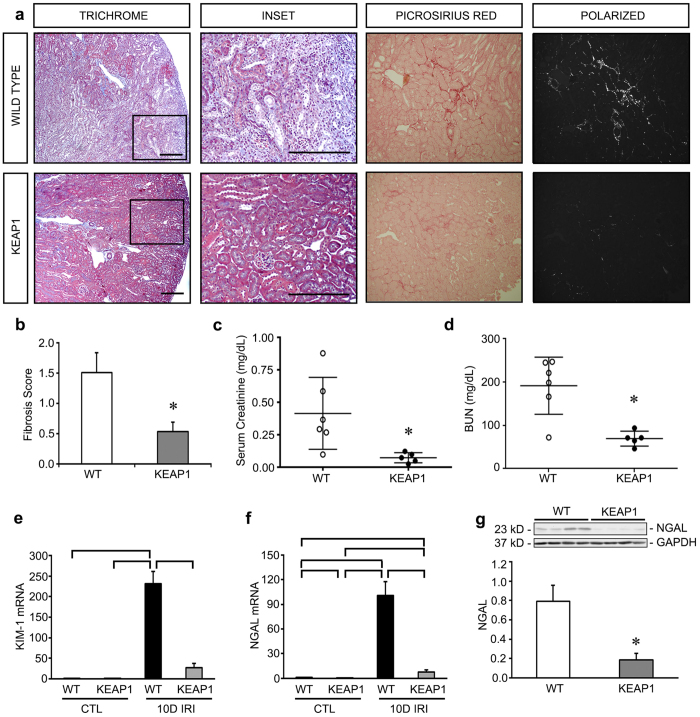
Figure 3. Keap1 hypomorphs demonstrated unequivocal protection 10 days after ischemia-reperfusion injury (IRI).
Keap1 hypomorphs (KEAP1) and wild type (WT) mice were subjected to unilateral renal IRI, with a contralateral nephrectomy performed 24 hours prior to sacrifice at 10 days. (a) Kidney sections were subjected to Masson’s Trichrome staining to evaluate for fibrosis development (collagen appears blue). WT mice also had more inflammatory cells. Low powered views are shown along with an enlarged inset of the boxed area. Bar equals 100 μm. Picrosirius red was also performed – under light microscopy collagen and other cellular components stain red. With polarized light of the same sections shown on light microscopy, birefringence is highly specific for collagen. (b) Keap1 hypomorphs had significantly decreased fibrosis, which was confirmed with fibrosis scoring (n = 5–6 for each group). (c,d) Serum creatinine and BUN were significantly reduced in the hypomorphs. Each dot represents an individual mouse with the mean ± SEM superimposed. (e,f) qRT-PCR for KIM-1 and NGAL shows significant reduction in these tubular injury markers in IRI KEAP1 kidneys compared to IRI WT kidneys. Brackets show significant differences, P < 0.05. (g) NGAL was significantly suppressed in the IRI KEAP1 kidneys compared to IRI WT kidneys, confirming the qRT-PCR result in (f). (P < 0.05, compared to similarly treated WT group).