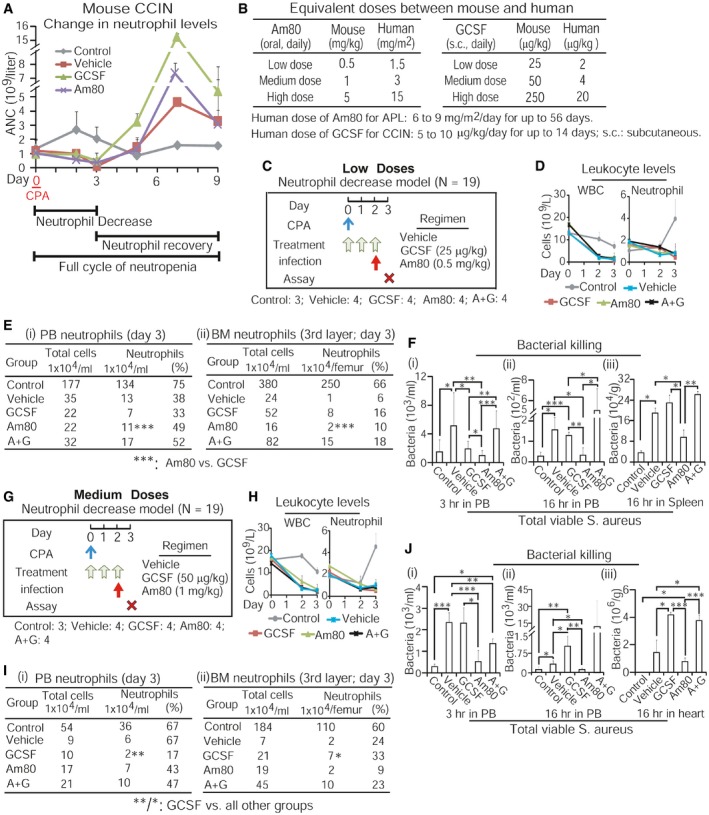
Mouse CCIN induced by cancer chemotherapy drug cyclophosphamide (CPA) consists of both neutrophil decrease and neutrophil recovery stages. ANC, absolute neutrophil count.
Equivalent low, medium, and high doses of Am80 and GCSF between human and mouse were calculated following FDA dose conversion guidelines.
Neutrophil decrease model with low‐dose treatment. After 4 h of CPA injection, mice were treated with regimens for 3 days. On day 2, mice were infected with 6 × 106 CFU of S. aureus via intravenous injection for up to 16 h before euthanasia. Control mice without CPA. N, numbers of mice.
Vetscan counting PB leukocytes.
Neutrophils induced by low‐dose treatment in PB (i) and BM (ii).
Bacterial killing by PB neutrophils was assessed at 3 and 16 h post‐infection and in spleen (i–iii), using blood agar analysis of total extracellular viable bacteria.
Neutrophil decrease model with medium‐dose treatment, using similar procedures described in panel (C).
Vetscan counting PB leukocytes.
Neutrophils induced by medium‐dose treatment in PB (i) and BM (ii).
Similar to panel (F), bacterial killing by PB neutrophils was evaluated 3 and 16 h post‐infection and in heart.
Data information: Data are shown as mean ± SD. These data represent: 1) two independent low dose tests with similar results; and 2) one time of low and medium dose test performed in parallel. *
‐test). Exact
.