Figure 6. Am80‐GCSF reduces infection‐related mortality in CCIN mice undergoing perpetual systemic intravenous bacterial infection throughout a full cycle of mouse CCIN.
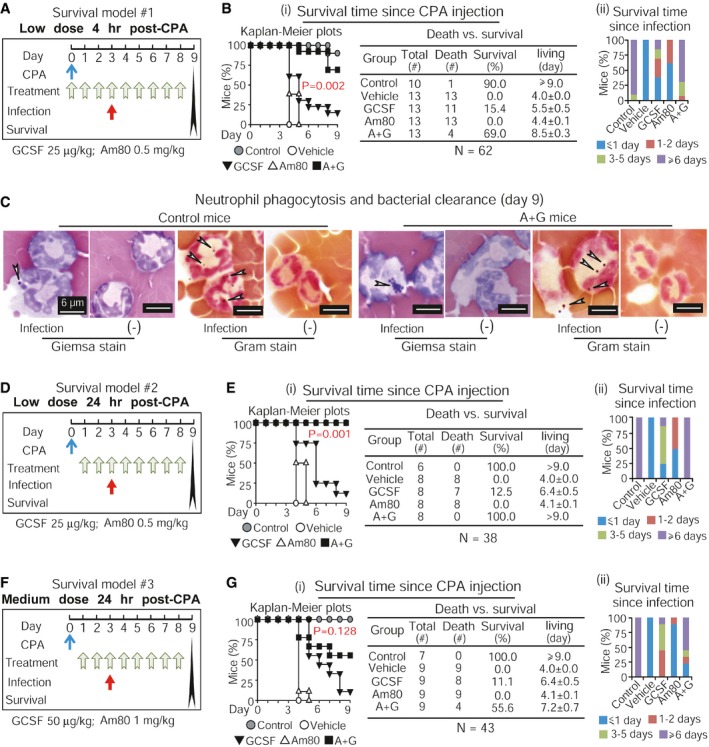
- Survival model #1 with low‐dose treatment after 4 h of CPA injection. Mice were infected with 5 × 106 CFU of S. aureus via intravenous injection on day 3. Moribund mice were euthanized and recorded as deceased on the day of euthanasia. Control mice without CPA.
- Survival of CCIN mice was calculated with both Kaplan–Meier plots and log‐rank test on day 9 since CPA injection (i) as well as assessed 6 days post‐infection (ii). Data represent three independent experiments with similar results.
- Gram and Giemsa stains analyzed neutrophil phagocytosis and bacterial clearance in mice surviving on day 9. White arrows indicate phagocytosed S. aureus in neutrophils.
- Survival model #2 with low‐dose treatment after 24 h of CPA injection. Other schedules/procedures were the same to those described in (A).
- Survival of CCIN mice was calculated with both Kaplan–Meier plots and log‐rank test on day 9 since CPA injection (i) as well as assessed 6 days post‐infection (ii). Data represent two independent experiments with similar results.
- Survival model #3 with medium‐dose treatment after 24 h of CPA injection. Other schedules/procedures were the same to those described in (A).
- Survival of CCIN mice was calculated with both Kaplan–Meier plots and log‐rank test on day 9 since CPA injection (i) as well as assessed 6 days post‐infection (ii). Data represent two independent experiments with similar results.
