Figure EV3. Characteristics of Drosophila CYLD.
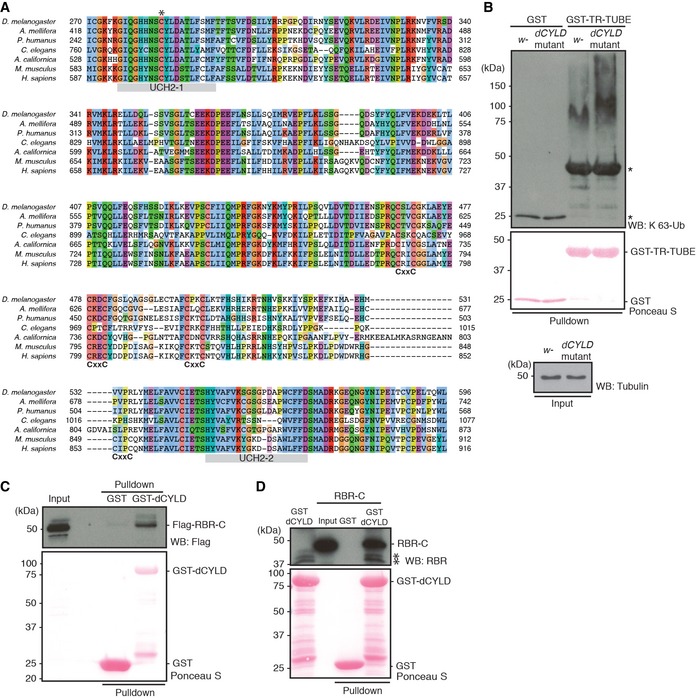
- A multiple amino acid sequence alignment of the CYLD catalytic domain in different species. * indicates predicted catalytic Cys residue, while C‐X‐X‐C pairs (labeled CxxC) and the UCH catalytic domains, UCH2‐1 and UCH2‐2 (in gray), are shown below the sequences.
- Endogenous level of K 63‐linked Ub chains in dCYLD mutant flies. Poly‐Ub chains in the total protein extracts of w − and dCYLD mutant were enriched by GST‐TR‐TUBE pulldown, and the samples were resolved and detected using anti‐K 63‐linked Ub chains. GST was used as control for the pulldown. Input of GST proteins was visualized by Ponceau S, and total protein extracts were blotted with anti‐tubulin antibody. *: nonspecific band.
- Interaction between dCYLD and LUBEL‐RBR‐C. Flag‐RBR‐C was transfected into S2 cells and total cell lysate was incubated with either agarose‐immobilized GST or GST‐dCYLD. After GST pulldown, samples were analyzed by immunoblotting using anti‐Flag antibody. Loading of GST proteins was visualized by Ponceau S staining.
- Protein–protein interaction of recombinant dCYLD and recombinant LUBEL‐RBR‐C. LUBEL‐RBR‐C purified from E. coli was incubated with immobilized GST or GST‐dCYLD for pulldown assay. The interaction was analyzed by immunoblotting using anti‐LUBEL‐RBR antibody. Loading of GST proteins was visualized by Ponceau S staining. *: nonspecific band.
