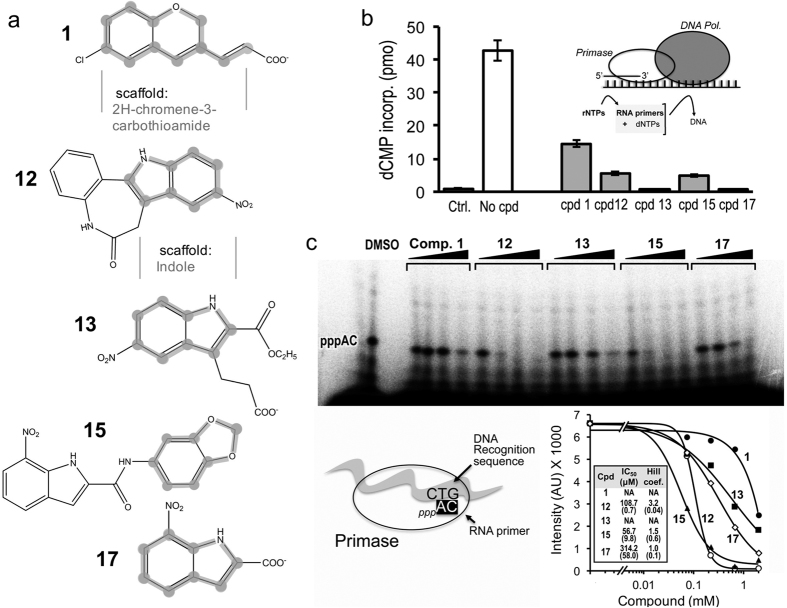
Figure 4. Small molecule inhibitors that contain fragments obtained by STD spectroscopy.
(a) Chemical structures of five small molecules obtained by virtual filtration using the ZINC database15 and high-throughput docking using AutoDock16 (list of 16 compounds presented in Fig. S1). The two subsets are based on the scaffolds obtained by STD spectroscopy: 2H-chromene-3-carbothioamide and indole (emphasized in thick grey). (b) Inhibitory effect of small molecules on bacteriophage T7 primase. Primase-dependent DNA synthesis. The reaction contained 0.3 mM dATP, dGTP, dCTP and [α–32P] dTTP (0.1 μCi), 100 μM ATP and CTP, 10 nM gp5/trx, 200 nM monomeric concentration of gp4A, 10 nM M13 ssDNA and 350 μM of each of the compounds. The reaction mixture was incubated for 30 min at 37 °C and spotted on DE81 filter paper. The amount of radioactivity remaining on the filter paper was measured (inset presents experimental setup). The amounts of RNA–primed DNA syntheses were determined by measuring the incorporation of dTMP (see Methods). The error bars were derived from three independent experiments. (c) Template-directed pppAC ribonucleotide synthesis catalyzed by T7 DNA primase. Reaction conditions involve incubating the primase domain with an oligonucleotide containing a primase recognition sequence. In this assay (bottom left), the DNA template containing the primase recognition site 5′-GTCA10-3′ enables the synthesis of only diribonucleotides pppAC. The reaction also contained [α-32P] CTP, ATP, and increasing amounts of the tested compounds (1.1, 3.3 and 10 μM). After incubation, the radioactive products were analyzed by electrophoresis through a 25% polyacrylamide gel containing 3 M urea and visualized using autoradiography (Fig. S2b presents results for all compounds). Bottom right: Quantification of gel bands representing the reaction products (5′-pppAC-3′).