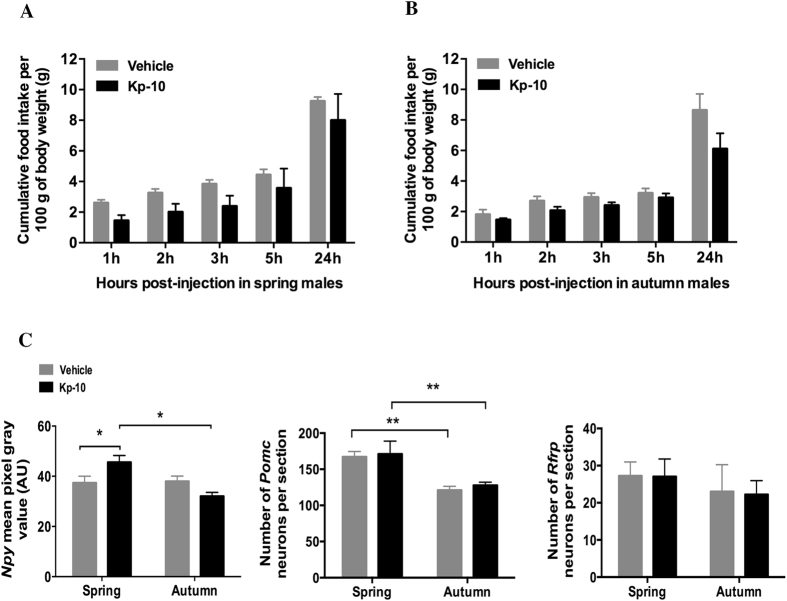
Figure 2. Effect of acute central injection of Kp10 on food intake and expression of genes encoding hypothalamic peptides NPY, POMC and RFRP-3, in 48 hours fasted male jerboas at spring and autumn.
(A,B) Cumulative food intake (g food intake/100 g body weight) measured 1 h, 2 h, 3 h, 5 h, and 24 h following icv injection of 4 μg Kp10 or vehicle (NaCl 0.9%) in 48 h-food deprived male jerboas captured in spring (A) or autumn (B). Statistical evaluation was performed using two-way repeated measures ANOVA followed by Student-Newman-Keuls test; data are expressed as mean ± SEM (n = 4 per group). No significant difference was observed between Kp10 and vehicle injected jerboas. (C) Semi-quantitative analysis of the labeling intensity of Npy mRNA in the arcuate nucleus (upper left panel), and quantitative measure of the number of neurons expressing Pomc mRNA in the arcuate nucleus (upper middle panel) and Rfrp mRNA in the dorso/ventro medial hypothalamus (upper right panel) 1h30 after 4 μg Kp10 (black bars) or vehicle (grey bars) icv injections in spring and autumn female jerboas. Statistical evaluation was performed using two-way ANOVA followed by a post hoc Holm-Sidak test; data are presented as mean ± SEM (n = 4 per group). *p < 0.05 for significant differences between Kp10 and vehicle injected group and **p < 0.01 for differences between spring and autumn groups. A.U: arbitrary unit.