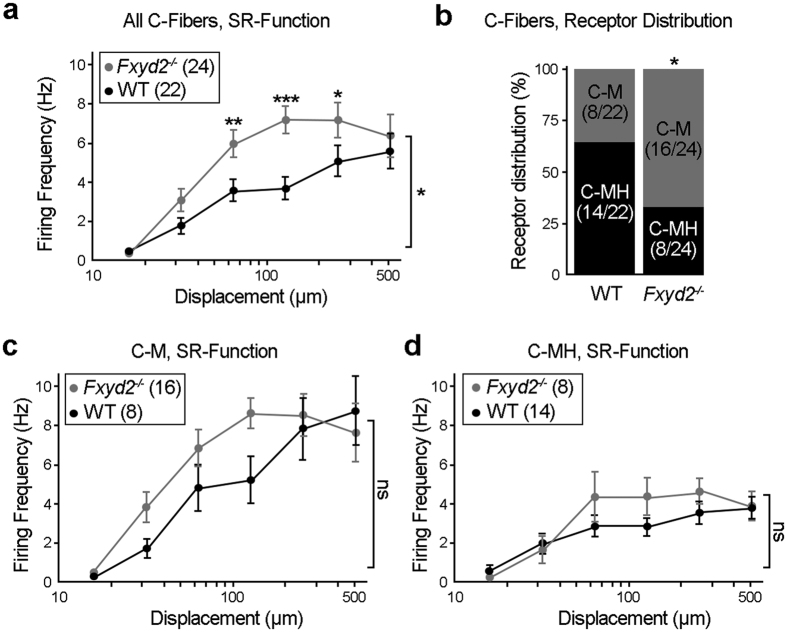
Figure 3. Impaired response properties of C-fiber nociceptor subtypes in Fxyd2−/− mutants.
(a) An ascending series of displacements (16–512 μm) using a constant stimulus velocity were used to mechanically stimulate C-fibers from WT and Fxyd2−/− mice. Mean firing frequencies were plotted as function of displacement amplitudes. Note that globally, mutant C-fibers are significantly more sensitive to suprathreshold mechanical stimuli compared to controls. (b) Distribution of C-M and C-MH fibers recorded in WT and Fxyd2−/− animals. The proportion of C-M vs C-MH was significantly increased in Fxyd2−/− mice (36% in Fxyd2+/+ vs 67% in mutants). (c,d) An ascending series of displacements (16–512 μm) using a constant stimulus velocity were used to mechanically stimulate C-fibers identified as C-Ms (g) or C-MHs (h) from WT and Fxyd2−/− mice. Mean firing frequencies were plotted as function of displacement amplitudes. Data are represented as mean ± SEM; numbers indicate fibers recorded. Statistical analyses were performed by Two-way ANOVA with Bonferoni post-hoc test in (a,c,d) and Chi-squared test in (b). ns: not significant; *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001.